ATMOSPHERIC TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY PROFILE RETRIEVALS BASED ON BP NEURAL NETWORK AND GENETIC ALGORITHM
-
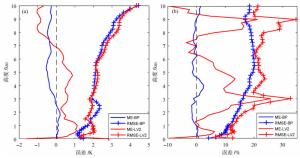
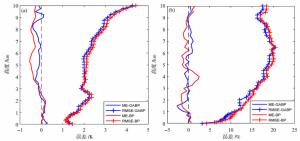
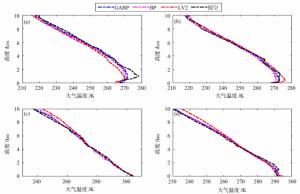
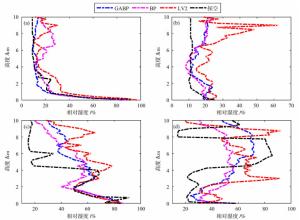
摘要: 为提高地基微波辐射计大气探测精度,融合BP神经网络与遗传算法,研究0~10 km大气温湿度廓线。首先,结合数据特征,基于数值模拟技术,建立一套TP/WVP-3000型号地基微波辐射计的一级数据质量控制和订正模型。然后,为减小训练样本代表性误差对模型反演精度的影响,利用遗传算法优化训练样本数据,建立一套精度更高的神经网络大气温湿度反演模型。最后,利用构建的反演模型,开展大气温湿度反演试验,结合探空资料和微波辐射计二级产品,评价反演模型精度。研究结果表明:(1)经过质量控制后的实测数据与模拟数据之间的相关性有显著提升;(2)经过质量控制与订正后建立的神经网络模型对比原微波辐射计二级产品的反演精度有一定提升,温度提升6.77%,湿度提升20.11%;(3)经过遗传算法优化后的训练样本所建立的神经网络反演模型对比原微波辐射计二级产品反演精度有进一步的提升,温度提升10.21%,湿度提升23.75%,反演结果与该地区同类型研究结果相比有着较大提升。Abstract: In order to improve the sounding accuracy of ground-based microwave radiometer, the atmospheric temperature and humidity profiles of 0-10km are studied by combining BP neural network and genetic algorithm. Firstly, based on numerical simulation technology, a set of level 1 data's quality control and correction model of TP/WVP-3000 ground-based microwave radiometer is established. Then, in order to reduce the influence of training sample errors on the accuracy of retrieval model, genetic algorithm is used to optimize training sample data, and a set of more accurate neural network to retrieve atmospheric temperature and humidity is established. Finally, the model is used to carry out atmospheric temperature and humidity retrieval experiments, and then experiment results are combined with sounding data and microwave radiometer's level 2 data to evaluate the accuracy of the retrieval model. Results show that: (1) the consistency between the measured data and the simulated data after quality control is significantly improved; (2) Compared with the level2 data of microwave radiometer, the retrieval accuracy of the neural network model after quality control and correction has a certain improvement, including a 6.77% improvement in temperature and a 20.11% improvement in humidity; (3) Compared with the level2 data of microwave radiometer, the retrieval accuracy of the neural network retrieval model based on the genetic algorithm optimized training sample has a further improvement, including a 10.21% improvement in temperature improved and a 23.75% improvement in humidity. Slightly superior results are achieved with our algorithm.
-
Key words:
- microwave radiometer /
- genetic algorithm /
- BP neural network /
- atmospheric profile /
- quality control
-
表 1 质控前后各通道模拟亮温与观测亮温相关系数
频率/GHz 22.2 23.0 23.8 26.2 30.0 51.3 52.3 53.9 54.9 56.7 57.3 58.8 R2质控前 0.97 0.97 0.96 0.91 0.79 0.72 0.78 0.99 1 1 1 1 R2质控后 0.98 0.98 0.97 0.95 0.85 0.80 0.86 0.99 1 1 1 1 表 2 各通道实测亮温与模拟亮温线性拟合方程
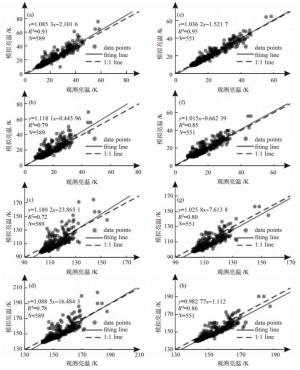
通道频率/GHz 线性拟合方程 22.24 y=0.980 5x-0.639 4 23.04 y=0.974 7x-0.280 3 23.84 y=0.961 7x-0.280 1 26.24 y=1.036 2x-1.521 7 30.00 y=1.015 0x-0.662 4 51.25 y=1.025 8x-7.613 8 52.28 y=0.982 8x-1.112 0 53.85 y=0.940 7x+11.595 0 54.94 y=0.986 7x+3.255 4 56.66 y=1.007 8x-2.360 8 57.29 y=1.008 5x-2.520 5 58.80 y=1.002 5x-0.997 0 -
[1] 王颖, 黄勇, 黄思源.大气温湿廓线反演问题的研究[J].国土资源遥感, 2008, 20(1): 23-26. [2] 朱雅毓.地基微波辐射计数据的综合质量控制与效果分析[D].南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2014. [3] 郭伟, 王振会, 孙安平, 等.地基微波辐射计网络资料处理系统设计及实现[J].气象, 2010, 36(4): 120-125. [4] 敖雪, 王振会, 徐桂荣, 等.微波辐射计亮温观测质量控制研究[J].气象科学, 2013, 33(2): 130-137. [5] 李青, 胡方超, 楚艳丽, 等.北京一地基微波辐射计的观测数据一致性分析和订正实验[J].遥感技术与应用, 2014, 29(4): 547-556. [6] SÁNCHEZ J L, POSADA R, GARCíA-ORTEGA E, et al. A method to improve the accuracy of continuous measuring of vertical profiles of temperature and water vapor density by means of a ground-based microwave radiometer[J]. Atmos Res, 2013, 122(3): 43-54. [7] 李娜, 张武, 陈艳, 等.基于微波辐射计的大气温湿廓线遥感探测[J].兰州大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 51(1): 61-71. [8] WANG Z, LI Q, HU F, et al. Remote sensing of lightning by a ground-based microwave radiometer[J]. Atmos Res, 2014, 150(1): 143-150. [9] 黄兴友, 张曦, 冷亮, 等.基于MonoRTM模型的微波辐射计反演方法研究[J].气象科学, 2013, 33(2): 138-145. [10] YANG L, GUAN LI. Study on the inversion of clear sky atmospheric humidity profiles with artificial neural network[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2011. 37(3):318-324. [11] 刘亚亚, 毛节泰, 刘钧, 等.地基微波辐射计遥感大气廓线的BP神经网络反演方法研究[J].高原气象, 2010, 29(6): 1 514-1 523. [12] 曹雪芬.地基微波辐射计亮温观测数据处理及对闪电高温的响应探讨[D].南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2013. [13] BAO Y S, CAI X, QIAN C, et al. 0~10 km temperature and humidity profiles retrieval from ground-based radiometer[J]. J Trop Meteor, 2018, 24(2): 243-252. [14] 张容容.基于BP神经网络的多通道微波辐射计大气参数反演算法[D].武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017. [15] 武广号, 文毅, 乐美峰.遗传算法及其应用[J].应用力学学报, 2000, 23(6): 9-10. [16] 丁霞, 黄兴友, 王海涛.太赫兹频段雷达探测的冰云微物理参数反演算法模拟研究[J].热带气象学报, 2019, 35(1): 63-72. [17] 张诚忠, 薛纪善, 冯业荣, 等.基于贝叶斯方案的雷达反射率反演水汽及其同化试验[J].热带气象学报, 2019, 35(2):145-153. [18] 肖辉, 万齐林, 刘显通, 等.基于WRF-EnKF系统的雷达反射率直接同化对台风"天鸽"(1713)预报的影响[J].热带气象学报, 2019, 35(4):433-445. [19] 王振会, 徐培源, 邓军, 等.三通道微波辐射计遥感大气中水汽、液水和电长度增量的数值实验[J].大气科学学报, 1995, 18(3): 396-403. [20] 杨贤为.气候应用专用数据库气象资料的质量检验[J].气象, 1998, 24(12): 33-36. [21] 张文刚, 徐桂荣, 廖可文, 等.降水对地基微波辐射计反演误差的影响[J].暴雨灾害, 2013, 32(1): 70-76. [22] 魏重, 雷恒池, 沈志来.地基微波辐射计的雨天探测[J].应用气象学报, 2001, 12(z1): 65-72. [23] 鲍艳松, 钱程, 闵锦忠, 等.利用地基微波辐射计资料反演0~10 km大气温湿廓线试验研究[J].热带气象学报, 2016, 32(2): 163-171. -





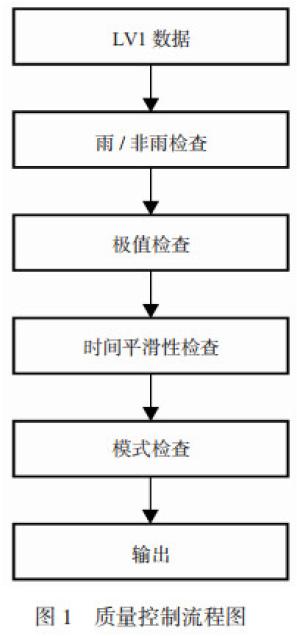
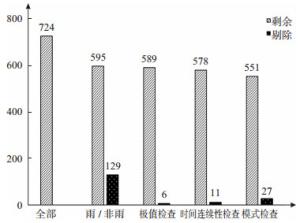
 下载:
下载:
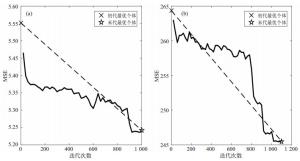


 粤公网安备 4401069904700003号
粤公网安备 4401069904700003号