REMOTE SENSING OF ARTIFICIALLY TRIGGERED LIGHTNING WITH GROUND-BASED MICROWAVE RADIOMETER
-
摘要: 为了深入研究雷电产生的微波热辐射特征,从2016年初夏开始利用地基微波辐射计在中国气象局雷电野外科学实验基地开展了连续4年的观测实验,根据雷电热效应的特征,制定了观测方案,并为地基微波辐射计设置了“引雷观测模式”。结果表明,地基微波辐射计具有对雷电热效应产生响应的能力。2017—2019年,辐射计一共成功捕获了30次人工触发闪电,观测效率逐年增长,平均为71.4 %;微波亮温脉冲幅度的最大值约125 K。结合其中28次触发事件的雷电流数据,分析了亮温脉冲幅度和雷电流积分量之间的相关性,并发现了最大亮温脉冲幅度与总电流作用积分之间可能存在指数关系。根据亮温观测数据估算了雷电热效应的持续时间,平均约0.5 s,其中25次触发事件的雷电流热效应持续时间与雷电流持续时间变化较为一致,相关系数约0.73。Abstract: In order to study the characteristics of microwave thermal radiation produced by lightning, we used ground-based microwave radiometer to carry out 4-year observation experiments at the Guangzhou Field Experiment Site for Lightning Research and Testing since the early summer of 2016. According to the general characteristics of lightning heating effect, the observation scheme and the lightning observation mode are established. The results show that the ground-based microwave radiometer has the ability to respond to the lightning heating effect. From 2017 to 2019, the radiometer has successfully captured 30 artificially triggered lightning events, the observation efficiency has increased year by year, with an average of 71.4 %, and the maximum amplitude of microwave brightness temperature pulse can reach about 125K. Based on the lightning current data of 28 triggered lightning events, the correlation between the brightness temperature pulse amplitude and the lightning current integral value is analyzed, and there may be an exponential relationship between the maximum brightness temperature pulse amplitude and the total current action integral. Based on the observational data of brightness temperature, the duration of lightning heating effect is estimated to be about 0.5s on average. It is found that the lightning heating effect duration of 25 triggered lightning events is consistent with the change of lightning current duration, and the correlation coefficient is about 0.73.
-
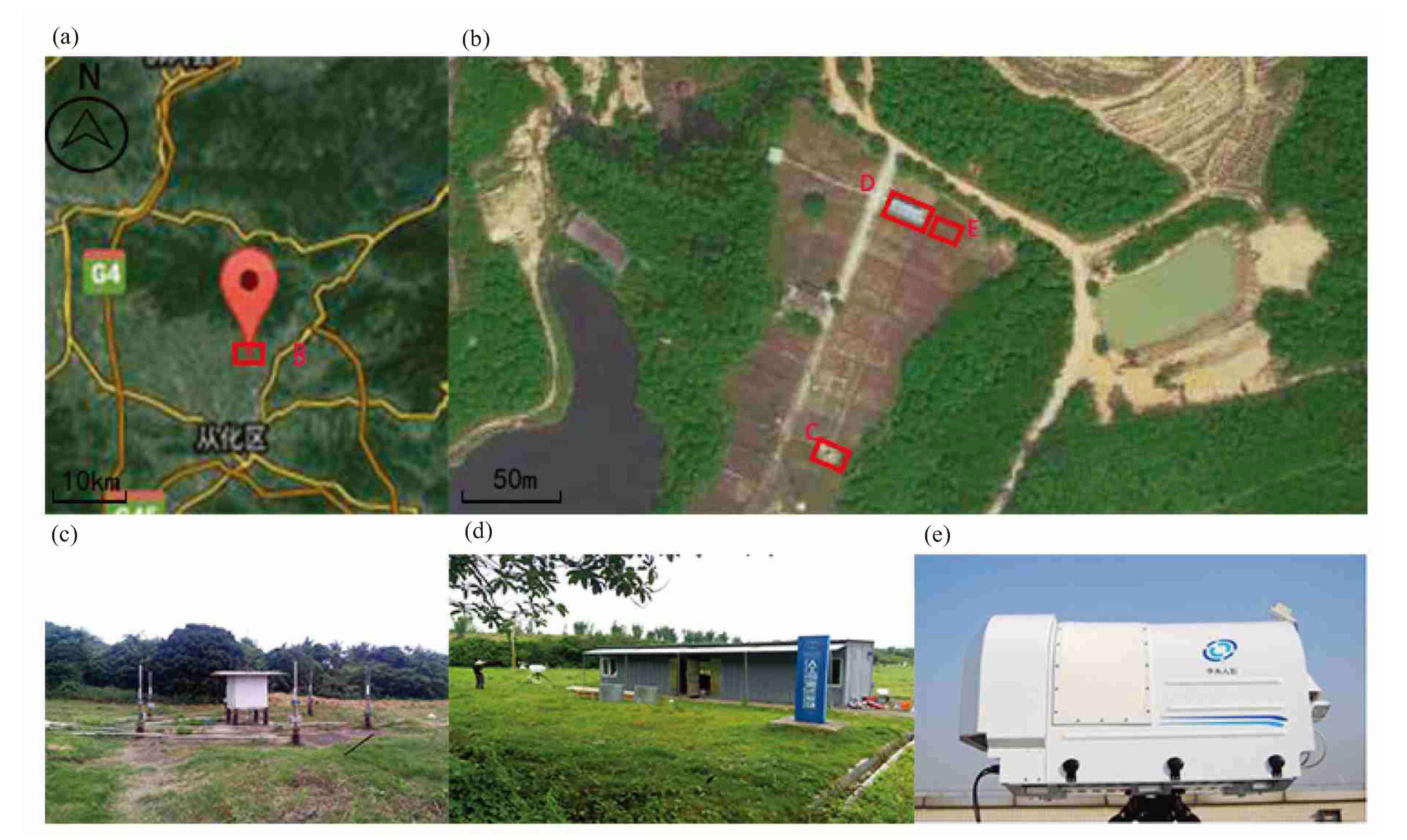
图 1 地基微波辐射计的安装位置示意[50]
a. 实验地点(B);b. 引雷场(C), 控制室(D)和地基微波辐射计(E);c. 引雷场;d.控制室;e. 地基微波辐射计。
图 3 4次人工触发闪电事件中闪电电流、亮温脉冲的脉冲幅度(Tba)、雷电流作用积分(I)和电荷量(Q)的时间序列图[52]
a. 2017/07/10 15:07:22.368;b. 2018/07/07 16:25:39.622;c. 2018/06/26 11:48:18.580;d.2019/06/11 13:14:31.312。
表 1 2017—2019年引雷观测模式下辐射计的工作参数
年份 日期 采样脉冲宽度(s) 观测频率
(GHz)仰角(°) 目的 单频 地面气象要素 2017 06/03-06/16 0.15 2.4 22.5; 30; 51.25; 56.66 30 1、寻求最佳仰角与最佳观测频率;
2、提高时间分辨率06/16 0.17 0.19 26.235; 30; 51.25; 56.66 66 06/16-07/16 0.17 0.19 28; 30; 51.25; 51.75 73.5 2018 05/26-07/26 0.15 0.17 30 30 1、进一步提高时间分辨率;
2、减小地面气象要素采样频次及影响2019 06/04-07/07 0.15 0.17 26.235;30 30 获取闪电距离信息[48] 表 2 2017—2019年辐射计的观测效率
年份 成功触发事件次数 辐射计产生响应的事件次数 辐射计观测效率(%) 2017 11 7 63.6 2018 13 9 69.2 2019 18 14 77.8 2017—2019 42 30 71.4 表 3 2017—2019年亮温脉冲的脉冲幅度统计表
年份 最大亮温脉冲幅度(K) 平均亮温脉冲幅度(K) 总电流作用积分的平均值(A2s) 2017 73.8 12.2 42341 2018 125.4 29.8 42590 2019 48.9 8.8 27317 2017—2019 82.4 16.9 37416 -
[1] ORVILLE R E. A high-speed time-resolved spectroscopic study of the lightning return stroke: Part Ⅰ. A qualitative analysis. [J]. J Atmos Sci, 1968, 25(5): 827-838. [2] ORVILLE R E. A high-speed time-resolved spectroscopic study of the lightning return stroke: Part Ⅱ. A quantitative analysis. [J]. J Atmos Sci, 1968, 25(5): 839-851. [3] ORVILLE R E. A high-speed time-resolved spectroscopic study of the lightning return stroke: Part Ⅲ. A time-dependent model[J]. J Atmos Sci, 1968c, 25(5): 852-856. [4] 冯桂力, 郄秀书, 吴书君. 山东地区冰雹云的闪电活动特征[J]. 大气科学, 2008, 32(2): 289-299. [5] 刘冬霞, 郄秀书, 冯桂力. 华北一次中尺度对流系统中的闪电活动特征及其与雷暴动力过程的关系研究[J]. 大气科学, 2010, 34(1): 95-104. [6] KONG X, YANG Z, ZHANG T, et al. Optical and electrical characteristics of in-cloud discharge activity and downward leaders in positive cloud-to-ground lightning flashes[J]. Atmos Res, 2015, 160: 28-38. [7] LITTELL J S, MCKENZIE D, PETERSON D L, et al. Climate and wildfire area burned in western U. S. ecoprovinces, 1916-2003[J]. Ecological Applications, 2009, 19: 1 003-1 021. [8] FLANNIGAN M, CANTIN A S, DE GROOT W J, et al. Global wildland fire season severity in the 21st century[J]. Forest Ecology & Management, 2013, 294, 54-61. [9] GIGLIO L, RANDERSON J T, VAN D W G R, et al. Global estimation of burned area using MODIS active fire observations[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2006, 6: 957-974. [10] BORUCKI W J, CHAMEIDES W L. Lightning: Estimates of the rates of energy dissipation and nitrogen fixation[J]. Reviews of Geophysics. 1984, 22: 363-372. [11] FRANZBLAU E. Electrical discharge involving the formation of NO, NO2, HNO3 and O3[J]. J Geophy Res, 1991, 96: 22 337-22 345. [12] COORAY V, RAHMAN M. Efficiencies for production of NOx and O3 by streamer discharges in air at atmospheric pressure[J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 2005, 63: 977-983. [13] WANG Y, DESILVA A, GOLDENBAUM G, et al. Nitric oxide production by simulated lightning: Dependence on current, energy, and pressure[J]. J Geophy Res, 1998, 103: 149-159. [14] LEVY Ⅱ H, MOXIM W J, KLONECKI A A, et al. Simulated tropospheric NOx: Its evaluation, global distribution and individual source contributions[J]. J Geophy Res, 1999, 104(D21): 26279-26306. [15] 周筠珺, 郄秀书, 言穆弘, 等. 雷暴过程中闪电产生NOx的地面观测研究[J]. 高原气象, 2003, 22(3): 275-280. [16] FIEUX R P, GARY C H, HUTZLER B P, et al. Research on artificially triggered lightning in France[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, 1978, PAS-97(3): 725-733. [17] DEPASSE P. Statistics on artificially triggered lightning[J]. J Geophy Res Atmos, 1994, 99(D9): 18 515-18 522. [18] 刘欣生, 张义军, 郄秀书. 人工引雷及其在雷电防护中的应用[J]. 电网技术, 1997, 5: 31-35. [19] 樊艳峰, 陆高鹏, 蒋如斌, 等. 利用低频磁场天线遥感测量人工引雷中的初始连续电流[J]. 大气科学, 2017, 41(5): 1 027-1 036. [20] 瞿海燕, 张廷龙, 潘慧玲. 回击电流及热效应与闪电光谱和通道温度的相关性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2014, 32(1): 10-16. [21] 王瑞燕, 袁萍, 岑建勇, 等. 闪电通道温度诊断中观测距离的影响[J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63(9): 099203-7. [22] 李青, 雷连发, 王振会, 等. 雷电流热效应的遥感观测研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017(5): 481-487. [23] ZHANG H, YUAN P, ZHANG Y, et al. Plasma characteristic of lightning discharge channel[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2013, 39(10): 2 452-2 458. [24] ZHIVLYUK Y N, MANDEL S S L. On the temperature of lightning and force of thunder[J]. Soviet Phys JETP, 1961, 13(2): 338-340. [25] WEIDMAN C, BOYE A, CROWELL L. Lightning spectra in the 850- to 1400-nm near-infrared region[J]. J Geophy Res Atmos, 1989, 94 (D11): 13 249-13 257. [26] 袁萍, 欧阳玉花, 吕世华, 等. 青海地区闪电回击通道的温度特性[J]. 高原气象, 2006, 25(3): 503-508. [27] 赵学燕, 袁萍, 王杰, 等. 闪电消散过程等离子体温度衰减规律的理论研究[J]. 物理学报, 2009, 58(5): 3 243-3 247. [28] DONG C, YUAN P, CEN J, et al. The heat transfer characteristics of lightning return stroke channel[J]. Atmos Rese, 2016: 178-179: 1-5. [29] MU Y, YUAN P, WANG X, et al. Temperature distribution and evolution characteristic in lightning return stroke channel[J]. Journal of Atmospheric & Solar Terrestrial Physics, 2016, 145, 98-105. [30] 张国强, 袁萍, 岑建勇, 等. 闪电首次回击过程中通道温度与电导率的演化特征[J]. 原子与分子物理学报, 2015, 32(6): 1 078-1 084. [31] 瞿海燕, 袁萍, 张华明, 郄秀书. 闪电放电过程的近红外光谱及温度沿放电通道的演化特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(8): 2 508-2 513. [32] MADHULATHA A, RAJEEVAN M, VENKATRATNAM M, et al. Nowcasting severe convective activity over southeast India using ground-based microwave radiometer observations[J]. J Geophy Res Atmos, 2013, 118: 1-13. [33] 郭丽君, 郭学良. 利用地基多通道微波辐射计遥感反演华北持续性大雾天气温、湿度廓线的检验研究[J]. 气象学报, 2015, 73(2): 368-381. [34] 雷连发, 陈婷, 杨柳, 等. 微波辐射计在西安一次强对流天气过程的分析应用[J]. 火控雷达技术, 2017, 46(4): 63-66. [35] Pan Y, Shuang Z, Qing L, et al. Analysis of convective instability data derived from a ground-based microwave radiometer before triggering operations for artificial lightning. [J]. Atmos Res, 2020, 243: 105005. [36] 孙京, 蔡然, 柴健, 等. 基于微波辐射计和闪电观测资料估算对流性降水方法初探[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(3): 438-446. [37] CHAN W P. Performance and application of a multi-wavelength, ground-based microwave radiometer in intense convective weather[J]. Meteorol Z, 2009, 18(3): 253-265. [38] 苟阿宁, 韩芳蓉, 张文刚, 等. 地基微波辐射计观测资料在一次雷电潜势预报中的应用分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2018, 34(2): 126-136. [39] 曹治强, 刘辉志, 李万彪, 等. 中尺度对流系统的微波辐射和闪电特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 41(5): 731-739. [40] KATSANOS D K, LAGOUVARDOS K, KOTRONI V, et al. The relationship of lightning activity with microwave brightness temperatures and spaceborne radar reflectivity profiles in the central and eastern Mediterranean[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology & Climatology, 2009, 46(11): 2 700-2 708. [41] MAGI B I, WINESETT T, CECIL D J. Estimating lightning from microwave remote sensing Data[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology & Climatology, 2016, 55(9): 2 021-2 036. [42] GÜLDNER J, SPÄNKUCH D. Remote sensing of the thermodynamic state of the atmospheric boundary layer by ground-based microwave radiometry[J]. Journal of Atmospheric & Oceanic Technology, 2001, 18(6): 925-933. [43] SÁNCHEZ J L, POSADA R, GARCÍA-ORTEGA E, et al. A method to improve the accuracy of continuous measuring of vertical profiles of temperature and water vapor density by means of a ground-based microwave radiometer[J]. Atmos Res, 2013, 122(3): 43-54. [44] MASSARO G, STIPERSKI I, POSPICHAL B, et al. Accuracy of retrieving temperature and humidity profiles by ground-based microwave radiometry in truly complex terrain[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2015, 8(3): 3 355-3 368. [45] 张北斗. 地基多通道微波辐射计的反演算法及应用[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2014. [46] 朱磊, 卢建平, 雷连发, 等. 新型多通道微波辐射计及大气观测分析[J]. 火控雷达技术, 2014, 43(1): 84-88. [47] 张义军, 吕伟涛, 陈绍东, 等. 广东野外雷电综合观测试验十年进展[J]. 气象学报, 2016, 74(5): 655-671. [48] WANG Z, LI Q, HU F, et al. Remote sensing of lightning by a ground-based microwave radiometer[J]. Atmos Res, 2014, 150: 143-150. [49] 曹雪芬. 地基微波辐射计亮温观测数据处理及对闪电高温的响应探讨[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2013. [50] JIANG S, PAN Y, LEI L, et al. Remote sensing of the lightning heating effect duration with ground-based microwave radiometer[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2018, 205 (2018): 26-32. [51] 钱勇. 人工触发闪电上行先导的观测研究[D]. 南京: 成都信息工程大学, 2016. [52] JIANG S, WANG Z, LEI L, et al. Preliminary study on the relationship between the brightness temperature pulses observed with a groundbased microwave radiometer and the lightning current integral values[J]. Atmos Res, 2020, 245: 105072. [53] COORAY V. An Introduction to Lightning[M]. Netherlands: Springer Netherlands, 2015. -






 下载:
下载:






 粤公网安备 4401069904700003号
粤公网安备 4401069904700003号