A MULTI-ALGORITHM FUSION THUNDERSTORM SYSTEM RECOGNITION TECHNOLOGY BASED ON VLF/LF LIGHTNING DATA
-
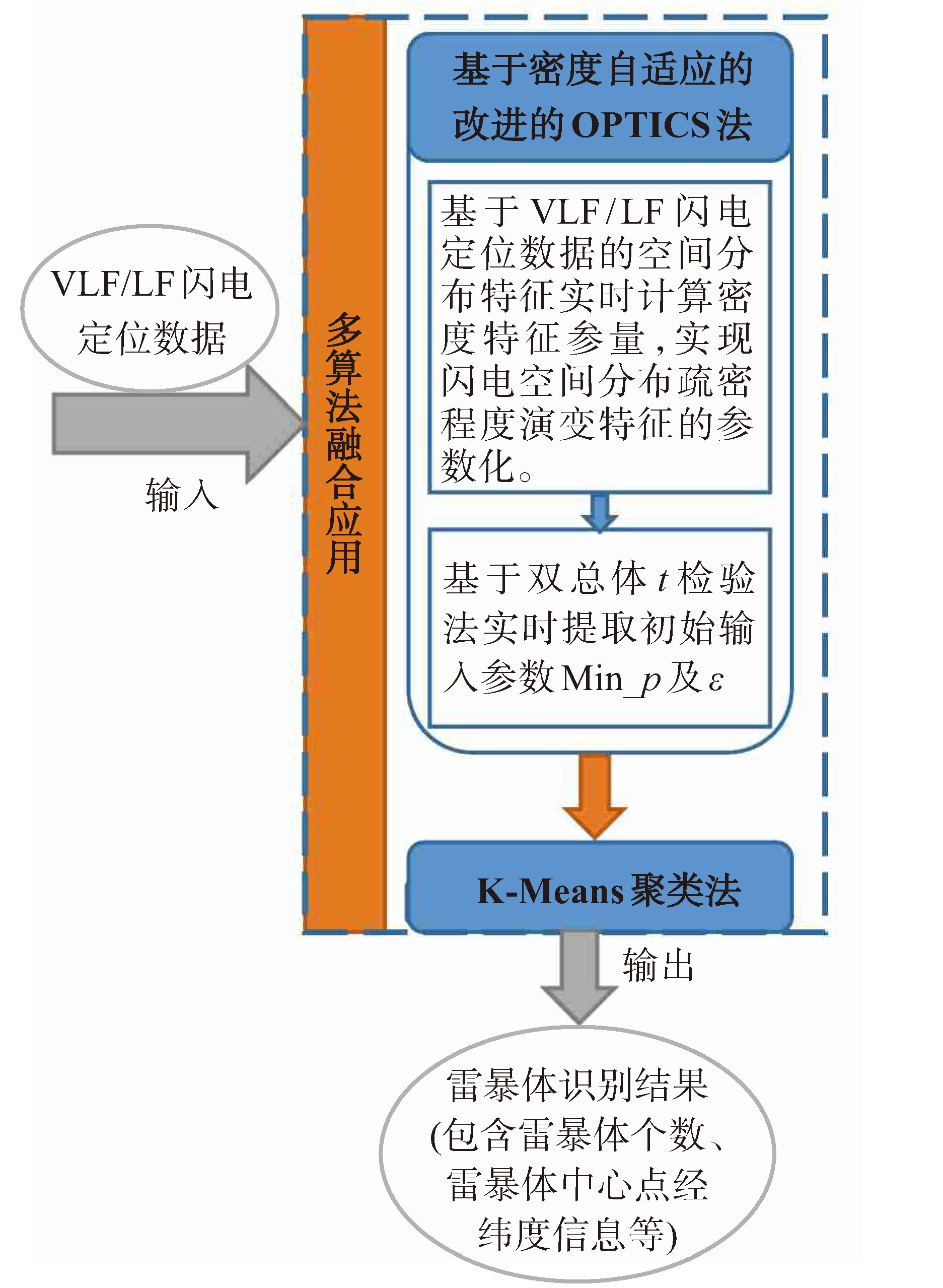
摘要: 为深入挖掘VLF/LF三维闪电监测网在雷电临近预警中的应用效益,提出一种基于VLF/LF闪电数据的多算法融合雷暴系统识别技术,首先对OPTICS聚类法进行参数自适应改进,即基于VLF/LF闪电数据的空间分布特征,利用双总体t检验法实时计算初始输入参数Min_ρ,使其自适应于待处理的闪电数据;而后与K-Means聚类法融合应用,利用K-Means法通过迭代计算聚类中心的优势,改进仅凭OPTICS法无法准确定位雷暴体的中心点的缺陷。经不同尺度雷暴天气过程检验,该技术有效改善OPTICS法等常规的密度聚类法无法适用于三维闪电数据聚类处理、无法识别区分密度差异不大的相邻雷暴体的缺陷,能实现任意尺度形状雷暴体的识别及中心点的精准计算,可为雷暴追踪及趋势外推工作提供优于传统聚类技术的雷暴系统识别结果,也能为雷暴灾害天气的预报及雷电预警模型的训练提供有效的知识库支撑。
-
关键词:
- VLF/LF闪电定位 /
- 参数自适应 /
- 多算法融合 /
- 雷暴识别 /
- 密度聚类
Abstract: In order to deeply explore the benefits of a VLF / LF 3D lightning monitoring network in lightning proximity warning, this paper proposes a multiple algorithm fusion thunderstorm system identification technique based on VLF / LF lightning data. First, the OPTICS clustering algorithm was improved to make it parameter-adaptive, i.e., the initial input parameters Min_ρ was calculated in real time by using the double total t-test method and the spatial distribution characteristics based on VLF / LF lightning data, making it adaptive to the lightning data to be processed. Then it was applied in combination with the K-Means clustering algorithm, whose advantages was able to calculate the cluster center iteratively to improve the defect that the center of thunderstorms cannot be accurately located by the OPTICS algorithm. Tested by thunderstorm weather processes on different scales, this technique effectively solves the defects of the conventional density clustering algorithms, e.g., the OPTICS algorithm can neither be applied to VLF/LF lightning data clustering processing nor distinguish adjacent thunderstorms with little difference in density. It identifies arbitrary scale shape thunderstorms and accurately calculates the centroid. Therefore this technique provides better thunderstorm system identification results for thunderstorm tracking and trend extrapolation compared with traditional clustering techniques, and also serves as an effective knowledge base support for severe thunderstorms forecasting and lightning warning model training. -
表 1 雷暴天气过程个例属性表
序号 时间 闪电数量 天气过程类型 检验目的 个例1 2020.7.10T19:20—30 2 168 区域性雷暴天气过程 ①检验聚类效果 ②检验单个时段的识别结果 个例2 2020.7.2T16:40—50 306 分散性雷暴天气过程 ①检验聚类效果 ②检验单个时段的识别结果 个例3 2020.7.9 T17:40—50 55 局地性雷暴天气过程 ①检验聚类效果 ②检验单个时段的识别结果 个例4 2020.7.10T18:10—10 26 827 区域性雷暴天气过程 检验连续时段雷暴系统运行轨迹识别结果 -
[1] 吕伟涛, 张义军, 孟青, 等. 雷电临近预警方法和系统研发[J]. 气象, 2009, 35(5): 10-17. [2] 王萍, 高毅, 李聪. 50KM以内雷暴系统的分类识别方法研究[J]. 气象, 2016, 42(2): 230-237. [3] KELLY W E, RAND T W, UCKUN S, et al. Image processing for hazard recognition in on-board weather radar: US, US6650275 B1[P]. US, 2023. [4] 侯荣涛, 朱斌, 冯民学, 等. 基于dbscan聚类算法的闪电临近预报模型[J]. 计算机应用, 2012, 32(3): 847-851. [5] 周康辉, 郑永光, 蓝渝. 基于闪电数据的雷暴识别、追踪与外推方法[J]. 应用气象学报, 2016, 27(2): 173-181. [6] 侯荣涛, 路郁, 王琴, 等. Optics算法在雷电临近预报中的应用[J]. 计算机应用, 2014, 34(1): 297-301. [7] 路郁. 聚类算法在雷电预警及雷灾分析中的应用[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2014. [8] 孟晓阳, 王佳权, 马启明, 等. 2020年基于VLF/LF三维闪电定位系统的全国闪电数据集[J]. 中国科学数据: 中英文网络版, 2022, 7(1): 31-44. [9] 郭润霞, 王迎春, 张文龙, 等. 基于VLF/LF三维闪电监测定位系统的北京闪电特征分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2018, 34(3): 393-400. [10] 成勤, 张科杰, 刘俊, 等. 一次特大暴雨过程三维和二维系统闪电特征对比分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2021, 37(3): 396-408. [11] 李兵, 周剑, 卜俊伟, 等. 木里县森林火灾原因分析及闪电监测资料应用[J]. 灾害学, 2021, 36(3): 125-130、159. [12] 孙明, 杨仲江, 钟颖颖, 等. 两种闪电资料的对比分析[J]. 电瓷避雷器, 2014(6): 109-114. [13] 崔雪东, 张卫斌, 王芳. 浙江省二维和三维闪电定位系统对比分析及效能评估[J]. 科技通报, 2020, 36(07): 14-20. [14] 朱彪, 曾金全, 李丹, 等. 三维地闪监测数据分析与校验[J]. 气象科技, 2018, 46(5): 868-874. [15] 张华明, 钱勇, 刘恒毅, 等. 山西省两套闪电定位系统地闪监测结果对比[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(2): 346-352. [16] 丁旻, 吴安坤, 刘芸. 两种闪电定位资料的对比分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(27): 47-54. [17] 曾勇, 丁旻, 罗雄, 等. 云贵高原斜坡过渡带一次大范围冰雹过程的闪电活动特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(5): 771-781. [18] 吴永斌, 赵晓兰, 胡颖, 等. 云南西双版纳地区闪电活动特征[J]. 大气科学学报, 2020, 43(4): 728-734. [19] 蒋尧, 孙豪, 杨敢, 等. 海南一次雷暴过程闪电特征分析[J]. 电瓷避雷器, 2022(3): 89-96. [20] 卢炳夫, 植耀玲, 伍华丽. 广西前汛期和后汛期地闪特征差异及影响因子分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2022, 41(2): 224-231. [21] 吴巍巍, 江聪世, 汤振鹏, 等. 基于时空聚类的雷电时空丛聚特性分析[J]. 高电压技术, 2016, 42(5): 1586-1593. [22] 卢炳夫, 植耀玲, 陈丹, 等. 广西VLF/LF和ADTD闪电定位系统对比分析[J]. 气象研究与应用, 2020, 41(2): 39-44. [23] 代声发, 黄启俊, 马启明. 基于粒子群算法的闪电定位网优化布站[J]. 武汉大学学报(理学版), 2017, 63(6): 506-512. [24] YANG Q, WANG J, ZHOU X, et al. Preliminary evaluation of Hai-Nan lightning detection network (HNLDN)[J]. Radio Science, 2021, 56 (9): 1-18. [25] 马启明, 苑尚博. 基于斜向通道的云闪放电特性研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(25): 6-11. [26] 韩丰, 沃伟峰. SWAN2.0系统的设计与实现[J]. 应用气象学报, 2018, 29(1): 25-34. [27] 龙柯吉, 康岚, 罗辉, 等. 四川盆地雷暴大风雷达回波特征统计分析[J]. 气象, 2020, 46(2): 212-222. [28] 王彦, 唐熠, 赵金霞, 等. 天津地区雷暴大风天气雷达产品特征分析[J]. 气象, 2009, 35(5): 91-96、135. [29] 纪晓玲, 王式功, 穆建华, 等. 宁夏雷暴天气过程划分及环流分型和环境场特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 2010, 21(3): 329-334. -






 下载:
下载:

















 粤公网安备 4401069904700003号
粤公网安备 4401069904700003号