Precipitation Forecasting Based on the Interpretability of Neural Network Models
-
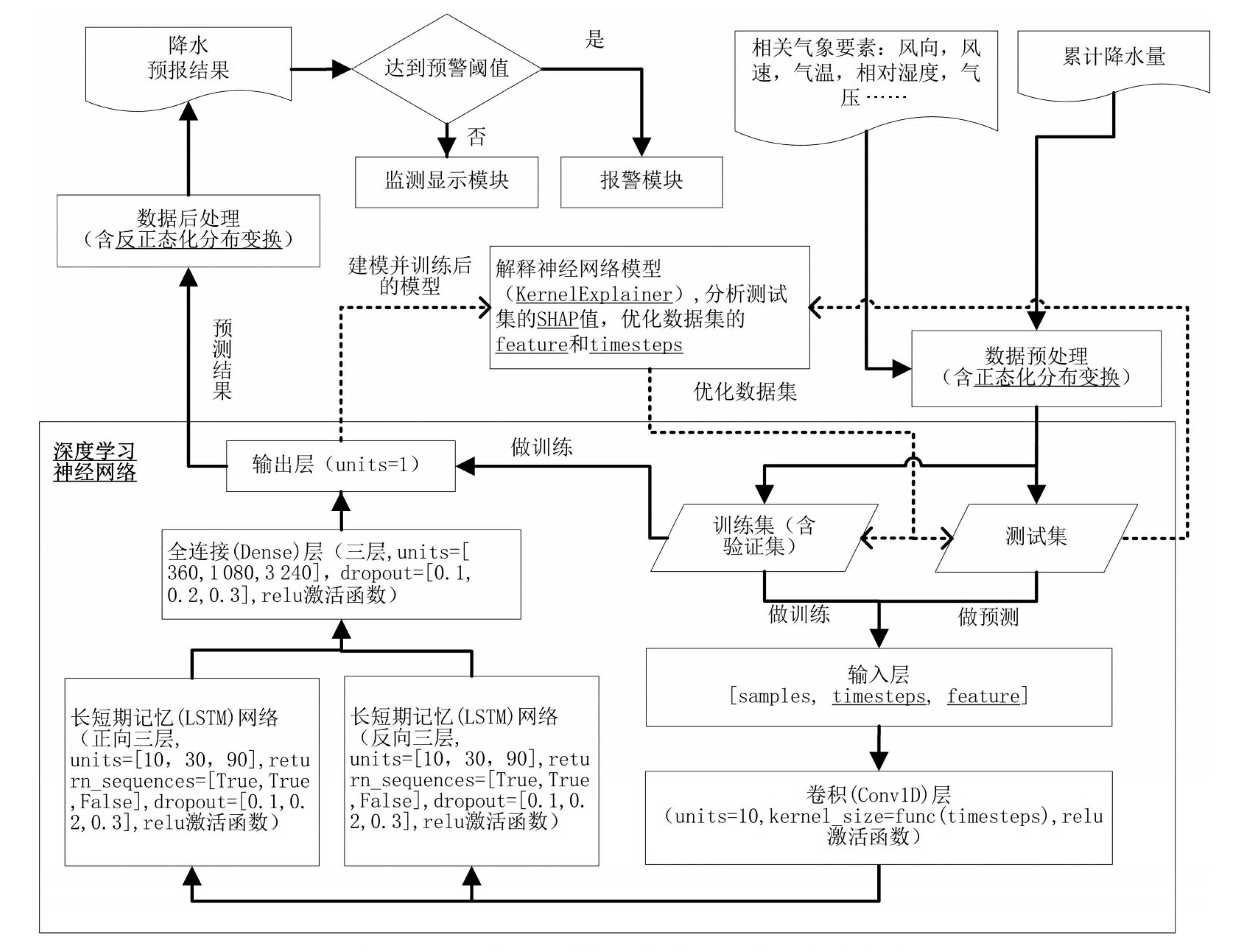
摘要: 为提高局地精细化预报的准确性和可靠性,提出了一种基于核函数KernelExplainer和可解释性“夏普值”(SHAP值)聚类分析的神经网络降水预报技术。该方法首先通过正态化分布变换解决神经网络的输出抖动问题,然后使用KernelExplainer估计由卷积(CNN)层、长短期记忆(LSTM)网络、全连接层构建的深度学习神经网络模型,并获取气象要素参数m和时间步长参数tl对于预测结果的贡献值SHAP,最后通过聚类分析SHAP值,在每次滚动预报中动态调整模型的m和tl参数,从而提高了无降水和强降水事件的预报效果。使用该方法基于2018年1月—2023年12月的观测和数值预报模式数据建立了南京信息工程大学大气观测基地的降水预报模型。实验证明,该方法相对于固定参数的深度学习神经网络模型、多层卷积长短期记忆网络(多层ConvLSTM)、模拟集合卷积神经网络(AnEn-CNN)和数值预报模式,降水平均绝对误差减少8%、7%、11% 和19%。Abstract: To improve the accuracy and reliability of localized, fine-scale precipitation forecasts, the present study proposed a new neural network capable of precipitation forecasting based on KernelExplainer and clustering of interpretable Shapley additive explanations (SHAP) values. First, the output jitter in the neural network was addressed by using normalized distribution transformation. Subsequently, we estimated the deep learning neural network model comprising convolutional (CNN) layers, long short-term memory (LSTM) networks, and dense layers using the KernelExplainer. This process yielded SHAP values that represent the contributions of meteorological parameter m and time step parameter tl to forecasting results. Finally, by dynamically adjusting the model's m and tl parameters through SHAP value clustering in each rolling forecast, we managed to use the method to improve forecasting performance for non-precipitation and heavy precipitation events. Using this method, a precipitation forecasting model for the Atmospheric Observation Station of Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology was established based on observational data and numerical weather prediction model outputs from January 2018 to December 2023. Experimental results show that, compared to fixed-parameter models, multilayer ConvLSTM models, Analog-Ensemble-CNN models, and numerical weather prediction models, the proposed model reduced the mean absolute error of precipitation forecasts by 8%, 7%, 11%, and 19%, respectively.
-
表 1 降水量的各模型预测误差比较
单位:mm。 气象要素 NDT+SHAP+DLNN DLNN 多层ConvLSTM AnEn-CNN EC插值 MAE RMSE MAE RMSE MAE RMSE MAE RMSE MAE RMSE 3小时降水 0.99 1.35 1.08 1.48 1.07 1.46 1.11 1.53 1.22 1.71 注:平均绝对误差MAE,均方根误差RMSE详见参考文献[29]。 表 2 降水量等级的各模型预测误差比较
单位:mm。 降水量等级[27, 30] NDT+SHAP+DLNN DLNN 多层ConvLSTM AnEn-CNN EC插值 MAE RMSE MAE RMSE MAE RMSE MAE RMSE MAE RMSE 无降水-微迹
(0~0.1 mm)0.02 0.05 0.17 0.26 0.17 0.27 0.19 0.31 0.05 0.10 小雨
(0.1~9.9 mm)1.06 1.37 1.08 1.44 1.06 1.40 1.15 1.57 1.23 1.75 中雨
(10~24.9 mm)2.08 2.47 3.03 3.56 2.89 3.31 3.20 3.79 4.43 4.87 大雨
(25~49.9 mm)5.38 5.57 8.50 8.65 7.91 8.12 8.79 9.02 10.54 10.91 暴雨或短时强降水
(50~99.9 mm)6.91 7.18 16.67 17.01 16.28 16.73 16.99 17.48 22.5 22.71 表 3 降水量的各模型预测有/无降水准确率比较
单位:%。 季节 NDT+SHAP+DLNN DLNN 多层ConvLSTM AnEn-CNN EC插值 准确率 TS评分 准确率 TS评分 准确率 TS评分 准确率 TS评分 准确率 TS评分 春季(3—5月) 83.3 42.8 64.7 25.1 66.0 26.5 62.3 24 79.5 36.6 夏季(6—8月) 62.6 31.7 48.8 22.9 50.4 24.9 47.1 21.5 58.4 26.3 秋季(9—11月) 83.8 36.2 66.9 21.8 68.2 23.3 64.9 20.7 79.9 30.8 冬季(12—2月) 87.5 43.6 68.3 25.2 69.5 26.6 65.8 24.2 83.2 37.6 表 4 降水量的各模型预测有/无强降水准确率比较
单位:%。 季节 NDT+SHAP+DLNN DLNN 多层ConvLSTM AnEn-CNN EC插值 准确率 TS评分 准确率 TS评分 准确率 TS评分 准确率 TS评分 准确率 TS评分 春季(3—5月) 100 无 100 无 100 无 100 无 100 无 夏季(6—8月) 99.9 50 99.9 0 99.9 0 99.9 0 99.9 0 秋季(9—11月) 100 100 99.9 0 99.9 0 99.9 0 99.9 0 冬季(12—2月) 100 无 100 无 100 无 100 无 100 无 表 5 2023年08月15日8时起报的3小时累计降水量预报结果比较
单位:mm。 模型名称 2023081511 2023081514 2023081517 2023081520 2023081523 2023081602 2023081605 2023081608 MAE NDT+SHAP+DLNN 55.229 6.339 6 3.696 4 0.873 4 0 0 0 0 1.542 4 DLNN 33.201 4.269 8 2.207 6 0.175 3 0.011 6 0.153 1 0.148 4 0.186 2 2.918 9 多层
ConvLSTM34.026 3.365 2.277 9 0.163 4 0.086 1 0.161 2 0.096 6 0.097 1 2.702 7 AnEn-CNN 32.933 4.126 6 2.427 0.179 2 0.002 8 0.160 4 0.100 7 0.138 4 2.950 3 EC插值 30.2 0.2 2.6 0 0 0 0 0 2.88 实测降水 51.6 0.7 1.5 0 0 0 0 0 0 表 6 2023年9月19日20时起报的3小时累计降水量预报结果比较
单位:mm。 模型名称 2023091923 2023092002 2023092005 2023092008 2023092011 2023092014 2023092017 2023092020 MAE NDT+SHAP+DLNN 0 1.901 5 59.221 7 3.035 1 0.592 3 2.123 4 0 0 1.889 9 DLNN 0.052 1 0.911 8 38.179 9 0.906 9 0.433 2 1.063 3 0.198 2 0.120 7 2.374 9 多层
ConvLSTM0.051 2 0.808 0 38.063 2 1.880 2 0.779 9 1.016 1 0.104 8 0.175 1 2.212 5 AnEn-CNN 0.073 3 0.184 4 38.662 8 0.902 1 0.490 2 0.389 2 0.099 4 0.190 7 2.300 4 EC插值 0 0 25.4 7.1 0.7 0 0 0 3.51 实测降水 0 0 50.0 5.6 1.3 1.4 0 0 0 表 7 两次强降水事件的动态参数
预测时间 气象要素(m_oc) 时间步长(tl_oc) 2023081511—2023081608 对流性降水(3 h,6 h,12 h),降水(3 h),露点温度(850 hPa,925 hPa,1 000 hPa,2 m),气压(500 hPa,850 hPa,925 hPa,1 000 hPa),温度(500 hPa,700 hPa,850 hPa,925 hPa,1000 hPa,2 m),比湿(850 hPa,925 hPa,1 000 hPa),相对湿度(700 hPa,850 hPa,925 hPa,1 000 hPa),风向风速(300 hPa,500 hPa,700 hPa,850 hPa,1000 hPa,10 m),高度(300 hPa,700 hPa,1 000 hPa),对流有效位能,K指数,垂直风切变,水汽通量散度(700 hPa,850 hPa,925 hPa,1 000 hPa),假相当位温(700 hPa,850 hPa,925 hPa,1 000 hPa) 5 2023091923—2023092020 对流性降水(3 h,6 h),降水(3 h,6 h),露点温度(850 hPa,925 hPa,1 000 hPa,2 m),气压(300 hPa,700 hPa,850 hPa,925 hPa,1 000 hPa),温度(500 hPa,850 hPa,925 hPa,1 000 hPa,2 m),风向风速(300 hPa,500 hPa,850 hPa,1 000 hPa,10 m),对流有效位能,K指数,垂直风切变,水汽通量散度(700 hPa,850 hPa,925 hPa),假相当位温(700 hPa,850 hPa,925 hPa),温度平流(300 hPa,500 hPa) 6 -
[1] 胡艳, 岳彩军, 顾问, 等. 台风"利奇马"(1909)影响期间上海强降水成因诊断分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2023, 39(6): 883-897. [2] 耿焕同, 吴正雪, 计浩军, 等. 基于GIS的上海市嘉定区暴雨积涝灾害风险区划研究[J]. 灾害学, 2015, 30(1): 96-101. [3] 翁莉, 马林, 徐双凤. 城市暴雨灾害风险评估及防御对策研究—以江苏省南京市为例[J]. 灾害学, 2015, 30(1): 130-134. [4] 杜惠良, 钮学新, 殷坤龙, 等. 浙江省滑波、泥石流气象条件分析及其预报研究[J]. 热带气象学报, 2005, 21(6): 642-65. [5] BENJAMIN S G, WEYGANDT S S, BROWN J M, et al. A North American hourly assimilation and model forecast cycle: the rapid refresh [J]. Mon Wea Rev, 2016, 144(4): 1 669-1 694. [6] 李泽椿, 谌芸, 张夕迪, 等. 中央气象台暴雨预报业务的发展及思考[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2019, 38(5): 407-415. [7] 苏翔, 袁慧玲. 集合预报统计学后处理技术研究进展[J]. 气象科技进展, 2020, 10(2): 30-41. [8] 田笑, 余文韬, 从靖, 等. 统计降尺度方法在天津小时降水和气温精细化预报中的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(1): 135-145. [9] 郑永光, 周康辉, 盛杰, 等. 强对流天气监测预报预警技术进展[J]. 应用气象学报, 2015, 26(6): 641-657. [10] 谌芸, 曹勇, 孙健, 等. 中央气象台精细化网格降水预报技术的发展和思考[J]. 气象, 2021, 47(6): 655-670. [11] 蒋薇, 刘芸芸, 陈鹏, 等. 利用深度神经网络和先兆信号的江苏夏季降水客观预测方法[J]. 气象学报, 2021, 79(6): 1 035-1 048. [12] CHEN H L. Time series interval forecast using GM(1, 1) and NGBM(1, 1) models[J]. Soft Comput, 2019, 23(5): 1 541-1 555. [13] SHA Y, GAGNE D J, WEST G, et al. A hybrid analog-ensemble-convolutional-neural-network method for postprocessing precipitation forecasts[J]. Mon Wea Rev, 2022, 150(6): 1 495-1 515. [14] 陈生, 黄启桥, 谭金凯, 等. 基于多尺度特征深度学习的短临降水预报[J]. 热带气象学报, 2023, 39(6): 799-806. [15] SHI X, CHEN Z, WANG H, et al. Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1506.04214, 2015. [16] 郭瀚阳, 陈明轩, 韩雷, 等. 基于深度学习的强对流高分辨率临近预报试验[J]. 气象学报, 2019, 77(4): 715-727. [17] YADAV N, GANGULY A R. A deep learning approach to shortterm quantitative precipitation forecasting[C]//CI2020: 10th International Conference on Climate Informatics, 2020: 8-14. [18] 孙健, 曹卓, 李恒, 等. 人工智能技术在数值天气预报中的应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 2021, 32(1): 1-11. [19] LUNDBERG S M, LEE S I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, California USA, 2017: 4 768-4 777. [20] LUNDBERG S M, ERION G, CHEN H, et al. From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees[J]. Nat Mach Intell, 2020, 2(1): 56-67. [21] 樊仲欣, 陈旭红, 谭桂容. 基于递归小波神经网络的江苏城镇夏季最高气温预报预警技术[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2019, 28(6): 56-69. [22] 陈怡然, 李进喜, 陈思洁, 等. 新能源环境下的太阳辐射预测系统[J]. 计算机仿真, 2023, 40(5): 140-144. [23] LIAO C, WANG I, LIN K P, et al. A fuzzy seasonal long short-term memory network for wind power forecasting[J]. Math, 2021, 9(11): 1-18. [24] 王耀庆, 孙建平, 李冰, 等. 基于小波变换和LSTM的短期风速预测研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2021, 38(2): 438-443. [25] 徐静萍, 王芳. 基于改进的S-ReLU激活函数的图像分类方法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(29): 12 963-12 968. [26] 罗俊然, 温蜜, 何蔚. 基于特征构建及CAE-LSTM的短期电量预测方法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2024, 41(2): 41-48, 137. [27] 孙继松. 短时强降水和暴雨的区别与联系[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2017, 36(6): 498-506. [28] 樊仲欣, 焦圣明, 谭桂容. 基于密度峰值聚类的气象灾害识别[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2023, 32(1): 171-182. [29] 徐曼, 乔颖, 鲁宗相. 短期风电功率预测误差综合评价方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2011, 35(12): 20-26. [30] 程向阳, 王凯, 刘岩. 气象灾害调查研究与实践[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2018: 8. [31] 俞小鼎. 短时强降水临近预报的思路与方法[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2013, 32(3): 202-209. -






 下载:
下载:













 粤公网安备 4401069904700003号
粤公网安备 4401069904700003号