Daily Temperature Prediction Model Based on DWT-CNN-LSTM
-
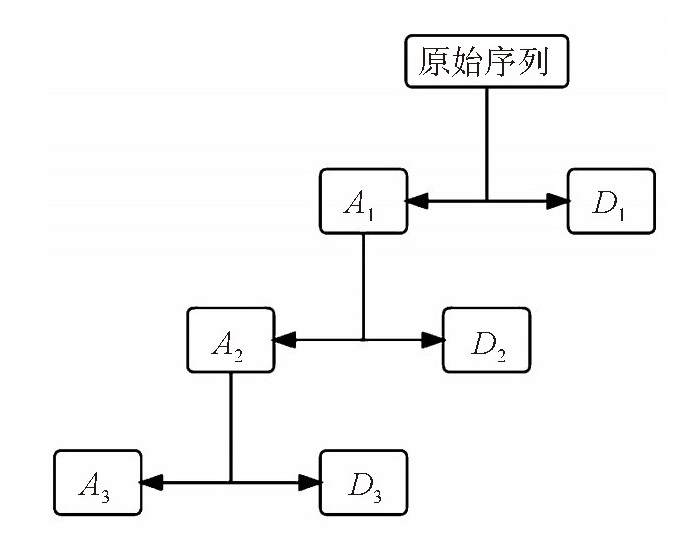
摘要: 气温的准确预测对人类生产生活、农业等方面至关重要。针对传统气温预测方法难以捕捉数据的动态变化、预测精度差等问题,提出了一种融合离散小波变换(Discrete Wavelet Transformation, DWT)、卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)和长短期记忆网络(Long Short-Term Memory, LSTM)的组合气温预测模型。首先,利用DWT对原始气温观测数据进行分解与重构;其次,使用CNN进行特征提取,使用LSTM对提取的特征信息进行处理,以实现气温预测。同时采用均方根误差、平均绝对值误差和决定系数作为评价指标;最后,使用气温观测数据验证所提模型的有效性,并分别与LSTM模型、CNN-LSTM模型和DWT-LSTM模型进行对比分析。实验结果表明,与LSTM模型、CNN-LSTM模型和基于离散小波变换的LSTM模型相比,DWT-CNN-LSTM模型分别将RMSE降低了1.009 24,1.002 74,0.100 23,MAE降低了0.918 36,0.862 65,0.144 89,R2提高了0.047 03,0.046 62,0.004 00,验证了该模型在气温预测中的有效性。这一结果为气温预测领域提供了新的参考依据,并有望在未来得到更广泛的应用。Abstract: Accurate temperature prediction is crucial for human production and life. To address the challenges of traditional temperature prediction methods, which struggle to capture dynamic data changes and often yield poor accuracy, this paper proposed a combined temperature prediction model that integrates discrete wavelet transform (DWT), convolutional neural network (CNN), and long short-term memory network (LSTM). First, the original temperature observation data were decomposed and reconstructed using the DWT. Second, the CNN was used to perform feature extraction, and the LSTM was applied to process the extracted feature information to achieve temperature prediction. Meanwhile, root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and coefficient of determination (R2) were used as the evaluation indexes. Lastly, temperature observation data were used to validate the effectiveness of the proposed model, and a comparative analysis was conducted using the LSTM model, the CNN-LSTM model, and the DWT-LSTM model. Experimental results show that, compared with the LSTM model, the CNN-LSTM model, and the LSTM model based on discrete wavelet transform, the DWT-CNN-LSTM model reduced the RMSE by 1.00924, 1.00274, and 0.10023, respectively, and the MAE by 0.91836, 0.86265, and 0.14489 respectively. It also improved R2 by 0.04703, 0.04662, and 0.00400 respectively. These findings confirm the effectiveness of the model in temperature prediction and provide a new reference for temperature prediction, indicating potential for broader future applications.
-
表 1 不同隐藏节点数的LSTM预测模型的预测结果
隐藏节点数 RMSE MAE R2 5 2.411 60 1.756 70 0.916 43 10 2.309 30 1.639 73 0.923 80 20 2.205 53 1.570 73 0.930 73 50 2.181 73 1.562 47 0.932 23 100 2.255 10 1.693 03 0.927 57 200 2.290 20 1.636 53 0.925 27 400 2.250 00 1.695 10 0.927 95 500 2.262 80 1.617 25 0.927 05 1 000 2.242 90 1.626 00 0.928 35 1 500 2.230 667 1.611 239 0.927 628 表 2 不同Conv1D层数的CNN-LSTM预测模型的预测结果
Conv1D层数 RMSE MAE R2 1 2.185 75 1.557 67 0.931 99 2 2.219 23 1.663 48 0.929 89 3 2.238 79 1.702 04 0.928 65 4 2.262 92 1.731 29 0.927 11 表 3 不同小波基函数和分解层数所对应的模型的预测结果
小波基函数 小波分解层数 RMSE MAE R2 sym2 1 1.903 28 1.368 73 0.947 80 2 1.617 96 1.043 72 0.961 41 3 1.657 27 1.270 84 0.957 93 4 1.320 66 0.773 00 0.972 50 5 1.284 45 0.769 31 0.973 40 sym4 1 1.766 32 1.264 61 0.955 14 2 1.473 13 0.957 77 0.968 00 3 1.363 67 0.821 40 0.971 62 4 1.269 46 0.802 37 0.974 49 5 1.243 66 0.739 13 0.975 13 sym6 1 1.768 26 1.172 99 0.955 07 2 1.414 68 0.915 58 0.970 59 3 1.302 72 0.773 99 0.974 07 4 1.240 52 0.843 45 0.975 64 5 1.230 76 0.834 30 0.975 64 sym8 1 1.718 45 1.265 00 0.957 57 2 1.418 34 0.891 77 0.970 38 3 1.324 14 0.868 07 0.973 19 4 1.236 19 0.741 62 0.975 84 5 1.287 05 0.808 61 0.973 38 表 4 不同模型的预测结果对比
预测模型 RMSE MAE R2 ARIMA 8.411 16 7.293 94 -0.007 69 指数平滑法 9.848 61 7.924 82 -0.381 55 DWT-CNN-LSTM模型 1.229 53 0.743 19 0.976 10 表 5 不同模型的预测结果对比
预测模型 RMSE MAE R2 LSTM模型 2.221 94 1.660 67 0.929 72 CNN-LSTM模型 2.215 44 1.604 96 0.930 13 DWT-LSTM模型 1.312 93 0.887 20 0.9727 5 DWT-CNN-LSTM模型 1.212 70 0.742 31 0.976 75 -
[1] 王强, 秦华旺, 齐春帅, 等. 基于自适应SA-PSO改进的XGBoost气温预测方法[J]. 电子测量技术, 2023, 46(7): 67-72. [2] AN H, LI Q, LV X, et al. Forecasting daily extreme temperatures in Chinese representative cities using artificial intelligence models[J]. Weather and Climate Extremes, 2023, 42: 100621. [3] PAPACHARALAMPOUS G, TYRALIS H, KOUTSOYIANNIS D. Predictability of monthly temperature and precipitation using automatic time series forecasting methods[J]. Acta Geophysica, 2018, 66(4): 807-831. [4] LI G, YANG N. A hybrid SARIMA‐LSTM model for air temperature forecasting[J]. Advanced Theory and Simulations, 2022, 6. [5] 唐湘玲, 刘卫平. 灰色预测模型在阿克苏地区气温预测中的应用[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 26(4): 411-414. [6] 陈岚, 文斌, 贺南, 等. 基于融合模型动态权值的气温预测[J]. 电子测量技术, 2022, 45(15): 68-74. [7] 杨建, 常学军, 姚帅, 等. 基于WT-CNN-BiLSTM模型的日前光伏功率预测[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18(8): 61-69, 79. [8] THI KIEU TRAN T, LEE T, SHIN J-Y, et al. Deep learning-based maximum temperature forecasting assisted with meta-learning for hyperparameter optimization[J]. Atmosphere, 2020, 11(5): 487. [9] 刘家辉, 梅平, 刘长征, 等. 基于GRU-CNN模型的云南地区短期气温预测[J]. 计算机仿真, 2023, 40(9): 472-476. [10] 李晶, 唐全莉. 基于1DCNN和LSTM的单站逐时气温预报方法[J]. 热带气象学报, 2022, 38(6): 800-811. [11] 陶晔, 杜景林. 基于随机森林的长短期记忆网络气温预测[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2019, 40(3): 737-743. [12] 唐旺, 马尚昌, 李程. 基于滑动窗口的LSTM地温预测方法[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 48(3): 377-384. [13] LIU H, YU C, YU C, et al. A novel axle temperature forecasting method based on decomposition, reinforcement learning optimization and neural network[J]. Adv Eng Informatics, 2020, 44: 101089. [14] 何利健, 张锐, 林晓冬. 基于DWT和双通道LSTM的卫星电池阵电流预测方法[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2023, 40(3): 415-421. [15] 王培力, 王瑞荣, 高鹏, 等. 基于离散小波变换与时间序列的钱塘江潮位预测[J]. 水电能源科学, 2016, 34(6): 6-8, 13. [16] 刘旭丽, 莫毓昌, 吴哲, 等. 基于DWT-CNN-LSTM的超短期光伏发电功率预测[J]. 郑州大学学报(理学版), 2022, 54(4): 86-94. [17] 王润英, 林思雨, 方卫华, 等. 基于CNN-LSTM的大坝变形组合预测模型研究[J]. 水力发电, 2024, 50(1): 37-41, 52. [18] 满轲, 武立文, 刘晓丽, 等. 基于CNN-LSTM模型的TBM隧道掘进参数及岩爆等级预测[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2024, 1-19. [19] 孟琪琳, 窦燕. 基于EMD-CNN-LSTM模型的铁路客运量短期预测研究[J]. 铁道运输与经济, 2023, 45(12): 65-73. [20] 那幸仪, 贾俊铖, 赵晓筠, 等. 基于小波变换和LSTM模型的城市天然气负荷预测[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2021, 38(12): 61-66. [21] 曹梅, 杨超宇. 基于小波的CNN-LSTM-Attention瓦斯预测模型研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2023, 19(9): 69-75 -






 下载:
下载:






 粤公网安备 4401069904700003号
粤公网安备 4401069904700003号