Satellite Cloud Image Nowcasting Based on CGAFNet
-
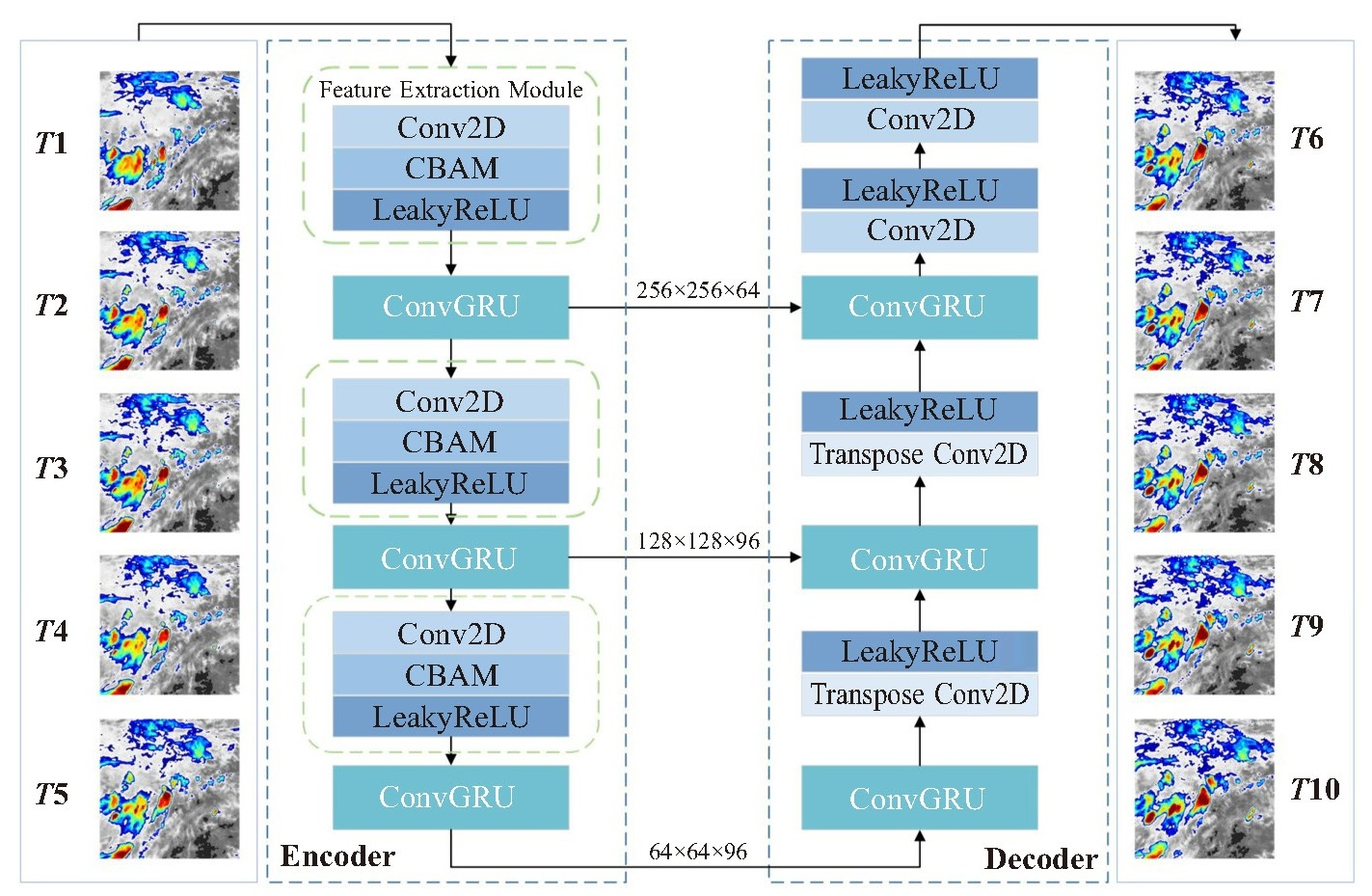
摘要: 卫星云图外推技术能及时掌握云团的运动轨迹和变化情况,为临近预报和灾害性天气的监测提供重要参考。然而,现有的云图预测方法存在难以捕捉小尺度云团发展、云图细节特征不清晰、预测结果逐渐模糊等问题,导致最终的预报效果不理想。为了有效提取卫星云图的时空信息,预报中小尺度云团的发展,利用FY-4A红外云图,以湖南区域为中心的中东部地区作为研究对象,从时空序列预测的角度出发,提出了一种卷积门控循环注意力融合网络(ConvGRU Attention Fusion Network,CGAFNet),并提出了主副损失(Primary and Secondary Loss,PaSLoss)作为模型的损失函数,构建了编-解码结构,更好地提取了卫星云图的时空信息。为验证网络框架的有效性,与三个典型网络进行对比实验,结果表明,CGAFNet在云图外推任务中均方根误差为10.00 K,结构相似性为0.74,峰值信噪比为31.43,该模型能准确预测云团的生消演变过程,在各项指标上均优于其它网络,证明该方法能获得更准确的预测精度,且具备良好的泛化能力。Abstract: Satellite cloud image extrapolation technology enables timely tracking of the movement and changes of cloud clusters, providing important references for nowcasting and severe weather monitoring. However, existing cloud image prediction methods face challenges such as difficulty in capturing the development of small-scale cloud clusters, unclear details in cloud images, and gradually blurred prediction results, leading to suboptimal forecasting performance. To effectively extract spatiotemporal information from satellite cloud images and forecast the development of mesoscale cloud clusters, this study utilized FY-4A infrared cloud images, focusing on the central and eastern regions of China with Hunan as the center. From the perspective of spatiotemporal sequence prediction, we proposed a convolutional gated recurrent attention fusion network (CGAFNet) and introduced primary and secondary loss (PaSLoss) as the model's loss function. An encoder-decoder structure was constructed to better extract spatiotemporal information from satellite cloud images. To validate the effectiveness of the network framework, we conducted comparative experiments with three typical networks. The results show that CGAFNet achieved a root mean squared error of 10.00 K, a structural similarity index of 0.74, and a peak signal-to-noise ratio of 31.43 in the cloud image extrapolation task. Outperforming other networks across various metrics, the model accurately predicted the evolution of cloud clusters, demonstrating that this method can achieve more accurate prediction accuracy and possesses good generalization ability.
-
Key words:
- satellite cloud image /
- nowcasting /
- spatiotemporal prediction /
- fusion network /
- attention mechanism
-
表 1 不同模型测试结果对比
方法 RMSE /K SSIM PSNR CGAFNet 10.00↓ 0.74↑ 31.43↑ GAN-CLSTM 10.58 0.69 31.1 ConvLSTM 10.16 0.71 30.91 Optical Flow 11.17 0.68 30.06 表 2 补充实验不同模型测试结果对比
方法 RMSE /K SSIM PSNR CGAFNet 9.78↓ 0.75↑ 31.46↑ GAN-CLSTM 10.14 0.74 31.22 ConvLSTM 9.95 0.7 30.09 Optical Flow 10.65 0.67 30.04 -
[1] 卢乃锰, 方翔, 刘健, 等. 气象卫星的云观测[J]. 气象, 2017, 43(3): 257-267. [2] HAMILL T M, NEHRKORN T. A short-term cloud forecast scheme using cross correlations[J]. Wea Forecasting, 1993, 8(4): 401-411. [3] 刘科峰, 张韧, 孙照渤. 基于交叉相关法的卫星云图中云团移动的短时预测[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2006, 11(4): 586-591. [4] 陈明轩, 王迎春, 俞小鼎. 交叉相关外推算法的改进及其在对流临近预报中的应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 2007, 18(5): 690-701. [5] GENKOVA I S, PACJEDJIEVA B, GANEV G, et al. Cloud motion estimation from METEOSAT images using time mutability method[J]. Laser Physics and Applications, 1999, 3 571: 297-301. [6] 吴剑坤, 陈明轩, 秦睿, 等. 变分回波跟踪算法及其在对流临近预报中的应用试验[J]. 气象学报, 2019, 77(6): 999-1 014. [7] 刘延安, 魏鸣, 高炜, 等. FY-2红外云图中强对流云团的短时自动预报算法[J]. 遥感学报, 2012, 16(1): 79-92. [8] VUKICEVIC T, GREENWALD T, ZUPANSKI M, et al. Mesoscale cloud state estimation from visible and infrared satellite radiances[J]. Mon Wea Rev, 2004, 132(12): 3 066-3 077. [9] VELDEN C S. Recent innovations in deriving tropospheric winds from meteorological satellites[J]. Rev Amer Meteor Soc, 2005, 36(2): 205-223. [10] 齐大鹏, 杨林, 周明飞, 等. 用改进的光流法和卫星TBB资料进行对流临近预报[J]. 热带气象学报, 2023, 39(1): 47-54. [11] 石玉立, 施声伟. 光流算法在FY-4A红外图像外推中的精度评价研究[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2021, 42(9): 150-158+224. [12] TURIEL, J. GRAZZINI, H. YAHIA. Multiscale techniques for the detection of precipitation using thermal IR satellite images[J]. IEEE GEOSCI REMOTE S, 2005, 2(4): 447-450. [13] SU X Y, LI T J, AN C, et al. Prediction of short-time cloud motion using a deep-learning model[J]. Atmosphere, 2020, 11(11): 1 151. [14] 肖海霞, 张峰, 王亚强, 等. 基于生成对抗网络和卫星数据的云图临近预报[J]. 应用气象学报, 2023, 34(2): 220-233. [15] TAN C, FENG X, LONG J W, et al. FORECAST-CLSTM: A new convolutional lstm network for cloudage nowcasting[C]//2018 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), 2018, 1-4. [16] 郑宗生, 刘敏, 胡晨雨, 等. 基于Seq2Seq和Attention的时序卫星云图台风等级预测[J]. 遥感信息, 2020, 35(4): 16-22. [17] 陶润喆. 基于风云4号卫星图像的西藏地区云检测和降水外推预报研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2021: 68-93. [18] 方巍, 庞林, 易伟楠. 基于深度时空融合网络的雷达回波外推模型[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(9): 2 526-2 538. [19] CHEN L F, LUO R, XING J, et al. Geospatial transformer is what you need for aircraft detection in sar imagery[J]. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens, 2022, 60: 1-15. [20] CHEN L F, WENG T, XING J, et al. Employing deep learning for automatic river bridge detection from SAR images based on adaptively effective feature fusion[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observations and Geoinformation, 2021, 102: 1-12. [21] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2018, 11211: 3-19. [22] SHI X J, GAO Z H, LAUSEN S L, et al. Deep learning for precipitation nowcasting: a benchmark and a new model[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017: 5 617-5 627. [23] MATTHEW C. DICKSON, ANNA S. BOSMAN, KATHERINE M. MALAN. Hybridised loss functions for improved neural network generalisation[J]. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, 2022, 405: 169-181. [24] 方巍, 李佳欣, 陆文赫. 基于3D卷积和自注意力机制的卫星云图预测研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2023, 59(1): 155-164. [25] SETIADI D I M. PSNR vs SSIM: Imperceptibility quality assessment for image steganography[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2021, 80(6): 8 423-8 444. [26] 张淼, 徐娜, 郑照军, 等. FY-3D MERSI-Ⅱ云顶产品算法及精度检验[J]. 热带气象学报, 2022, 38(6): 779-786. [27] 阮惠华, 张钧民, 许剑辉, 等. 考虑降水时间相关性的地面观测-雷达-卫星遥感逐时降水融合方法研究[J]. 热带气象学报, 2023, 39(3): 300-312. [28] 胡天慧, 余晖, 鲁小琴. 基于卫星遥感的热带气旋定强技术综述[J]. 热带气象学报, 2022, 38(2): 311-320. -






 下载:
下载:







 粤公网安备 4401069904700003号
粤公网安备 4401069904700003号