Analysis of Severe Hail Characteristics in Southern Fujian on 26 March 2022 Using Multi-Source radar
-
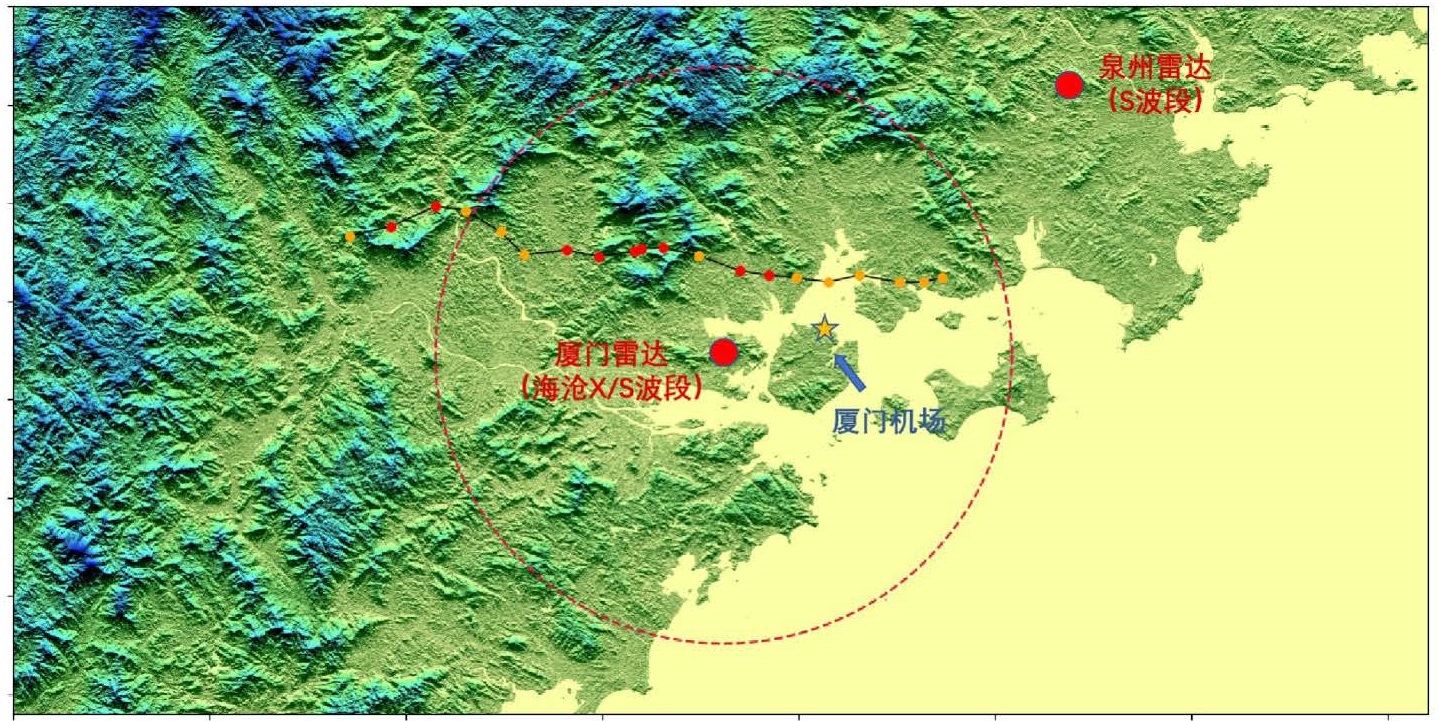
摘要: 利用福建厦门海沧X波段双偏振相控阵雷达、S波段多普勒双偏振天气雷达和福建泉州S波段多普勒单偏振天气雷达,结合常规气象观测资料,对2022年3月26日发生在闽南地区的一次冰雹过程进行分析,得到以下结论。(1)利用三部雷达对冰雹超级单体进行协同观测,可获得更加全面的雷达冰雹特征,有利于提高灾害性天气的预警能力。(2)厦门海沧X波段相控阵雷达完整观测到10 min内钩状回波演变形成的过程,ZDR弧、KDP足、ZDR环、CC环等双偏振特征体现出超级单体内粒子相态的变化。强回波后侧受衰减影响出现“V”型缺口甚至回波缺失,强回波区域内出现KDP洞表明该区域存在大冰雹。冰雹增长时,回波强度增强、ZDR和KDP大值区减少、CC降低;冰雹降落时,融化层附近ZDR增大、KDP显著增加、CC降低。(3)泉州S波段雷达观测到钩状回波、有界弱回波、三体散射、风暴顶辐散等经典冰雹特征;HT和VIL快速下降体现出冰雹降落的特征;中气旋的增强和减弱对于判断超级单体的强弱变化有较好的指示意义。(4)X波段相控阵雷达探测细腻程度优于海沧S波段雷达,在有效回波内KDP表现优于S波段雷达,在液态粒子探测方面X波段相控阵雷达更有优势。X波段相控阵雷达对15 dBZ以下和70 dBZ以上的回波探测能力低于S波段雷达,未探测到超级单体前侧的阵风锋,其探测强度较S波段雷达偏低约5~20 dBZ。
-
关键词:
- 冰雹 /
- X波段双偏振相控阵雷达 /
- 协同观测 /
- ZDR /
- KDP
Abstract: A supercell accompanied with severe hail in southern Fujian on 26 March 2022 is analyzed based on observations of Xiamen Haicang X-band dual polarization phased array radar, S-band Doppler dual polarization radar, and Quanzhou S-band Doppler radar, combined with conventional meteorological observation. The study yields the following results. (1) By using three radars for collaborative observation of hail supercells, more comprehensive radar hail characteristics can be obtained, which may improve the warning ability of severe weather. (2) The Haicang X-band phased array radar fully observs the process of hook shaped echo evolution within 10 minutes, and the dual polarization characteristics such as ZDR arc, KDP foot, ZDR ring, and CC ring reflect the changes in particle phase state within the supercell. The back of the strong echo is attenuated, resulting in V-shaped notches or even missing echoes. The appearance of KDP hole in the strong echo area indicates the presence of large hail. When hail grows, the echo intensity increases, the ZDR and KDP high value areas decrease, and CC decreases; When hail falls, ZDR increases, KDP significantly increases, and CC decreases near the melting layer. (3) Quanzhou S-band radar observs classic hail features such as hook shaped echoes, bounded weak echoes, three body scattering, and storm top divergence. The rapid decline of HT and VIL reflects the characteristics of hail falling. The strengthening and weakening of mesocyclones provide a good indicator for determining the strength changes of supercells. (4) The X-band phased array radar detection capability is better than that of Haicang S-band radar, and its KDP performance is better than that of S-band radar in effective echoes. X-band phased array radar has enhanced detection sensitivity in liquid particle detection. However, X-band phased array radar shows reduced detection capability for reflectivities below 15 dBZ and above 70 dBZ compared to the Haicang S-band radar, and the gust front of the supercell is not detected. Its detection intensity is about 5- 20 dBZ lower than that of S-band radar.-
Key words:
- hail /
- X-band dual polarization phased array radar /
- collaborative observation /
- ZDR /
- KDP
-
表 1 厦门海沧X波段双偏振相控阵雷达的主要技术指标
参数名称 X波段相控阵雷达参数值 参数名称 X波段相控阵雷达参数值 天线形式 一维阵列天线 雷达波长/cm 3.2 天线高度/m 393 峰值功率/W 300 工作频率/GHz 9.3~9.5 动态范围/dB ≥85 接收机噪声系灵敏/dB ≤3.3 脉冲宽度/μs 20 脉冲重复频率/Hz 400~4 000 径向分辨率/m 30 最大探测距离/km 42 水平波束宽度/° 3.6 仰角层数 12 垂直波束宽度/° 1.8 表 2 2022年3月26日08时厦门探空站强对流参数
时间 CAPE/(J·kg-1) K/℃ SI CIN/(J·kg-1) WBZ/km H-20℃/km 08:00 451.1 37.6 -0.24 0 4.2 7.9 -
[1] 俞小鼎, 姚秀萍, 熊廷南, 等. 多普勒天气雷达原理与业务应用[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2006. [2] CHURCH C R, DOSWELL C A, BURGESS D W. The tornado: Its structure dynamics prediction and hazards[M]. Boston: Wiley, 1993. [3] BROWNINGK A, LUDLAM F H, MACKLIN W C. The density and structure of hailstones[J]. Quart J Roy Meteor Soc, 1963, 89(379): 75- 84. [4] MARWITZ J D. The structure and motion of severe hailstorms. Part Ⅰ: Supercell storms[J]. J Appl Meteor, 1972, 11(1): 166-179. [5] 吴剑坤, 俞小鼎. 强冰雹天气的多普勒天气雷达探测与预警技术综述[J], 干旱气象, 2009, 27(3): 197-206. [6] WITT A, ELITS M D, STUMPF G J, et al. An enhanced hail detection al-gorithm for the WSR-88D[J]. Wea Forecasting, 1998, 13(2): 286- 303. [7] ZRNIC D S. Three-body scattering produces precipitation signature of special diagnostic value[J]. Radio Sci, 1987, 22(1): 76-86. [8] 张晓芳, 马中元, 王立志, 等. "2021-3-30"江西大冰雹超级单体的回波结构与关键机制分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2023, 39(3): 374-385. [9] 刁秀广, 李芳, 万夫敬. 两次强冰雹超级单体风暴双偏振特征对比[J]. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(4): 414-428. [10] 徐芬, 郑媛媛, 肖卉, 等. 江苏沿江地区一次强冰雹天气的中尺度特征分析[J]. 气象, 2016, 42(5): 567-577. [11] 刁广秀, 朱君鉴, 黄秀韶, 等. VIL和VIL密度在冰雹云判据中的应用[J]. 高原气象, 2008, 27(5): 1 131-1 139. [12] 郑媛媛, 俞小鼎. 一次典型超级单体风暴的多普勒天气雷达观测分析[J]. 气象学报, 2004, 62(3): 317-328. [13] 潘佳文, 蒋璐璐, 魏鸣, 等. 一次强降水超级单体的双偏振雷达观测分析[J]. 气象学报, 2020, 78(1): 86-100. [14] 吴举秀, 潘佳文, 魏鸣, 等. 不同尺寸冰雹S波段双偏振雷达偏振量特征统计[J]. 热带气象学报, 2022, 38(2): 193-202. [15] 曹舒娅, 孙伟, 韦芬芬, 等. 双偏振雷达在江苏"7.6"降雹过程中的应用分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 2021, 44(4): 549-557. [16] 刁秀广, 郭飞燕. 2019年8月16日诸城超级单体风暴双偏振参量结构特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 2021, 79(2): 181-195. [17] 马建立, 苏德斌, 金永利, 等. X波段双线性偏振雷达电磁波衰减对冰雹识别的影响[J]. 高原气象, 2012, 31(3): 825-835. [18] 胡志群, 刘黎平, 楚荣忠, 等. X波段双线偏振雷达不同衰减订正方法对比及其对降水估测影响研究[J]. 气象学报, 2008, 66(2): 251- 261. [19] 王晗, 刘黎平, 张扬. X波段双线偏振雷达不同衰减订正法对比分析[J]. 气象科技, 2018, 46(1) : 1-9. [20] 肖柳斯, 胡东明, 陈生, 等. X波段双偏振相控阵雷达的衰减订正算法研究[J]. 气象, 2021, 47(6): 703-716. [21] 苏永彦, 刘黎平. S波段双偏振雷达和X波段相控阵天气雷达中气旋识别结果对比[J]. 气象, 2022, 48(2): 229-244. [22] 汤兴芝, 俞小鼎, 熊秋芬, 等. 鄂西南冬末一次罕见的强冰雹过程分析[J]. 气象, 2022, 48(5): 618-632. [23] ANDRA D L. The origin and evolution of the WSR-88D mesocyclone recognition nomogram∥28th Conference on Radar Meteorology. Austin: Amer Meteor Soc, 1997, 364-365. [24] WITT A, NELSON S. The relationship between upper-level divergent outflow magnitude as measured by Doppler radar and hailstorm intensity// 22nd Radar Meteorology Conference. Boston: American Meteorology Society, 108-111. [25] 郭艳. 大冰雹指标TBSS在江西的应用研究[J]. 气象, 2010, 36(8): 40-46. [26] LEMON L R. The radar"three-body scatter spike": An operational large-hail signature[J]. Wea Forecasting, 1998, 13: 327-340. [27] ROMINE G S, BURGESS D, WIHELMSON R B. A dual-polarization-radar-based assessment of the 8 May 2003 Oklahoma city area tornadic supercell[J]. Mon Wea Rev, 2008, 136(8): 2 849-2 870. [28] KUMJIAN M R, RYZHKOV A V, MELNIKOV V M, et al. Rapid-scan super-resolution observations of a cyclic supercell with a dualpolarization WSR-88D[J]. Mon Wea Rev, 2010, 138(10): 3 762-3 786. [29] 潘佳文, 魏鸣, 郭丽君, 等. 闽南地区大冰雹超级单体演变的双偏振特征分析[J]. 气象, 2020, 46(12): 1 608-1 620. [30] KUMJIAN M R, RYZHKOV A V. Polarimetric signatures in supercell thunderstorms[J]. J Appl Meteor Climatol, 2008, 47(7): 1 940-1 961. [31] 刘黎平. 双线偏振多普勒天气雷达估测混合区降雨和降雹方法的理论研究[J]. 大气科学, 2022, 26(6): 761-772. [32] 陈龙, 唐明晖, 唐佳, 等. 湘东北一次降雹超级单体过程的双偏振雷达回波特征[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2023, 42(2): 211-222. [33] HALL M, GODDARD J, CHERRY S M. Identification of dydrometeors and other targets by dual-polarization radar[J]. Radio Science, 1984, 19(1): 132-140. [34] HUBBERT J, BRINGI V N, CAREY L D, et al. CSU-CHILL polarimetric radar measurements from a severe hail storm in eastern Colorado [J]. J Appl Meteor, 1998, 37(8): 749-775. -






 下载:
下载:












 粤公网安备 4401069904700003号
粤公网安备 4401069904700003号