Analysis of the 19 September 2023 EF3 Tornado in Funing, Jiangsu, and Multi-Band Radar Monitoring and Early Warning Techniques Ⅱ : Multi-Band Radar Feature and Early Warning
-
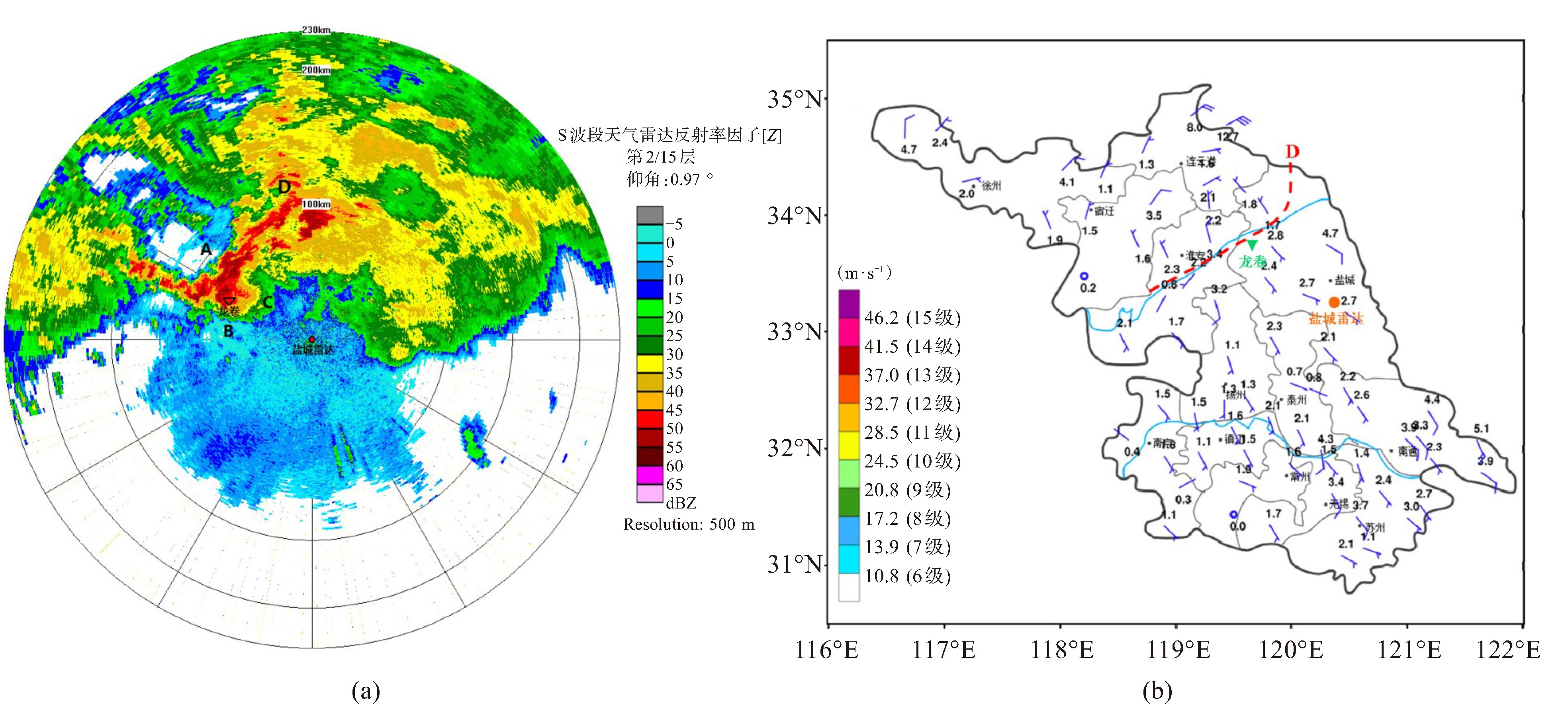
摘要: 为探究多波段雷达自适应协同观测在龙卷特征“捕捉”、业务预警中发挥的正向作用,构建可供业务参考的龙卷预警指标。本文以江苏历史上9月份罕见的2023年9月19日阜宁EF3级龙卷(简称“9.19”阜宁龙卷)案例为切入点,从多波段雷达回波特征分析、龙卷临近预警、预警效果检验3个方面展开讨论。(1) S波段和X波段天气雷达可互补式给出龙卷母体风暴及伴随龙卷发生的中小尺度特征。“9.19”阜宁龙卷雷达回波特征符合龙卷超级单体概念模型和成熟中气旋概念模型,并伴有龙卷风涡旋特征(TVS)、龙卷风碎片特征(TDS)、Zdr弧、Kdp弧、Zdr柱、Kdp柱、CC柱、W柱、反射率因子核(RC)等特征。(2) TDS与强劲的上升气流有关,中气旋与龙卷直接相关,两者均是龙卷发生的必要条件,均可作为龙卷临近预警指标。“9.19”阜宁龙卷TDS预警提前量为13 min和33 min,中气旋预警提前量为19 min和39 min。TDS高度还对龙卷的强度和维持有一定指示意义。(3) 经2023年9月19日江苏建湖EF1级龙卷过程预警检验,多波段雷达TDS和中气旋联合预警提前量达15 min。研究结果为江苏多波段天气雷达监测预警龙卷提供了参考依据。
-
关键词:
- “9.19”阜宁龙卷 /
- EF3级 /
- 多波段雷达 /
- 龙卷特征 /
- 龙卷预警
Abstract: To explore the value of adaptive cooperative observations from multi-band radar in capturing tornado features and improving operational warnings, and to construct a tornado warning index for operational reference, this study analyzes the rare EF3-level tornado case on 19 September 2023 in Funing, Jiangsu, which is a rare tornado event for September in the history of Jiangsu. The analysis is conducted from the multi-band radar echo characteristics, tornado nowcasting, and early warning verification. The key findings are as follows. (1) The S-band and X-band weather radars cooperate to provide meso- and micro-scale features of the tornado and its parent storm. Funing EF3-Level tornado convection pattern conforms to the tornadic supercell conceptual model and the mature mesocyclone conceptual model, exhibiting mesoscale features such as Tornado Vortex Signature (TVS), Tornadic Debris Signature (TDS), Zdr arc, Kdp arc, Zdr column, Kdp column, CC column, W column, and Reflectivity Core (RC). (2) Both the multi-band radar TDS, which is associated with strong updrafts, and the mesocyclone, which is directly linked to the tornado, can be used for tornado targeted warning. The lead warning time of Funing tornado using TDS is 13 min and 33 min, while the lead warning time of Funing tornado using mesocyclone is 19 min and 39 min. In addition, the height of TDS offers a certain indication of the intensity and maintenance of the tornado. (3) According to early warning test of Jianhu EF1-level tornado on 19 September, the combined warning of multi-band radar TDS and mesocyclonic characteristics reached a lead time of 15 min. These findings provide a reference for the multi-band weather radar monitoring and warning of tornadoes in Jiangsu.-
Key words:
- "9.19" Funing tornado /
- EF3-level /
- multi-band radar /
- tornado characteristics /
- tornado warning
-
表 1 临近预警指标效果检验表
S波段雷达观测时间 S波段雷达TDS特征 S波段雷达中气旋特征 X波段雷达中气旋特征 预警情况 提前量/min 距离裴桥村/km 面积/km2 顶高/m 最大负速度/(m·s-1) 切变值/s-1 旋转速度/(m·s-1) 顶高/m 21:12 / / / -15.3 7.38×10-3 16.1 5 907 21:08低层气旋式辐合,中高层中气旋 不预警 / 21:18 6.5(西) 3.75 1 286 -38.0 12.5×10-3 28.4 5 582 21:14低到中高层中气旋;加深加强 开始预警 15 21:24 / / / -53.6 17.32×10-3 36.0 4 653 21:20低到中高层中气旋;加深加强 保持预警 / 21:31 1.25(北) 1 743 -48.8 27.31×10-3 33.6 3 660 21:26低到中高层中气旋 保持预警 / 21:37 / / / -15.8 11.6×10-3 12.4 4 162 21:38低层无中气旋,中高层中气旋 解除预警 / -
[1] 范雯杰, 俞小鼎. 中国龙卷的时空分布特征[J]. 气象, 2015, 41(7): 793-805. [2] 俞小鼎, 赵娟, 范雯杰. 中国龙卷的时空分布与关键环境参数特征[J]. 热带气象学报, 2021, 37 (5/6): 681-692. [3] 冯佳玮, 闵锦忠, 庄潇然. 中国龙卷时空分布及其环境物理量特征[J]. 热带气象学报, 2017, 33(4): 530-539. [4] 郑永光, 刘菲凡, 张恒进. 中国龙卷研究进展[J]. 气象, 2021, 47(11): 1 319-1 335. [5] 郑永光. 中国龙卷气候特征和环境条件研究进展综述[J]. 气象科技进展, 2020, 10(6): 69-75. [6] 郑永光, 朱文剑, 姚聃, 等. 风速等级标准与2016年6月23日阜宁龙卷强度估计[J]. 气象, 2016, 42(11): 1 289-1 303. [7] 张小玲, 杨波, 朱文剑, 等. 2016年6月23日江苏阜宁EF4级龙卷天气分析[J]. 气象, 2016, 42(11): 1 304-1 314. [8] 张晶晶, 黄先香, 蔡康龙, 等. 2023年中国龙卷活动及灾情特征[J]. 气象科技进展, 2024, 14(1): 15-24. [9] 郑媛媛, 朱红芳, 方翔, 等. 强龙卷超级单体风暴特征分析与预警研究[J]. 高原气象, 2009, 28(3): 617-625. [10] 姚叶青, 郝莹, 张义军, 等. 安徽龙卷发生的环境条件和临近预警[J]. 高原气象, 2012, 31(6): 1 721-1 730. [11] 张一平, 梁俊平, 牛淑贞, 等. 豫东龙卷的环境条件和雷达监测预警分析[J]. 高原气象, 2020, 39(5): 1 089-1 101. [12] 俞小鼎. 强对流天气的多普勒天气雷达探测和预警[J]. 气象科技进展, 2011, 1(3): 31-41. [13] 曾强宇, 卿智鹏, 陈亚军, 等. 基于随机森林的组网雷达龙卷检测算法[J]. 热带气象学报, 2023, 39(6): 825-837. [14] 戴建华, 王国荣, 龚剑, 等. 梅雨锋中尺度涡旋内微型超级单体龙卷的形成研究[J]. 热带气象学报, 2021, 37(5): 693-709. [15] 王啸华, 郑媛媛, 濮梅娟, 等. 强天气综合报警追踪平台功能设计及龙卷预警中的应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 2018, 8(3): 61-69. [16] 姚聃. 龙卷预报预警体系建设—气象现代化的前沿挑战[J]. 气象科技进展, 2020, 10(6): 19-22. [17] 刘俊, 周红根, 刘新安, 等. 江苏北部龙卷雷达组网探测策略[J]. 气象科技, 2021, 49(2): 157-165. [18] 周红根, 李昭春, 孙强, 等. 江苏龙卷观测预警试验基地雷达网设计[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 2018, 6(8): 606-611. [19] 唐佳佳, 唐晓文, 徐芬, 等. "0612"高邮龙卷母体风暴演变特征分析及龙卷形成机理初探[J]. 热带气象学报, 2021, 37(5/6): 824-835. [20] 王琛, 魏鸣. 苏北2020年6月12日高邮龙卷的形成机理和回波演变分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2021, 37(5/6): 812-823. [21] 慕瑞琪, 吴海英, 李杨, 等. 2020年7月22日苏北地区EF2~EF3级龙卷天气分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2021, 37(5/6): 759-769. [22] 徐芬, 郑媛媛, 孙康远, 等. 江苏龙卷时空分布及风暴形态特征[J]. 气象, 2021, 47(5): 517-528. [23] 周晓敏, 郑永光. 2020年梅雨期江苏两次龙卷过程环境背景和龙卷母体风暴形态特征分析[J]. 气象科技进展, 2020, 10(6): 34-42. [24] GRAMS J S, THOMPSON R L, SNIVELY D V, et al. A climatology and comparison of parameters for significant tornado events in the United States[J]. Wea Forecasting, 2012, 27(1): 106-123. [25] 张玉洁, 苑文华, 徐百言. 江苏阜宁龙卷超级单体风暴的雷达资料分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 37 (3): 409-418. [26] MARKOWSKI P M. Hook echoes and rear-flank downdrafts: A review[J]. Mon Wea Rev, 2002, 130(4): 852-876. [27] 唐晓文, 李峰, 刘高平. 龙卷形成过程及母体风暴结构与演变研究进展[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 2018, 33(6): 599-605. [28] KUMJIAN M R, KAIN A P, BENMOSHE N, et al. The anatomy and physics of ZDR columns: Inverstigating a polarimetric radar fignature with a spectral bin microphysical model[J]. J Appl Meteorol Climatol, 2014, 53: 1 820-1 843. [29] 王炳赟, 魏鸣, 范广洲, 等. 1522强台风"彩虹"螺旋雨带中衍生龙卷的超级单体演变与机理研究Ⅰ: 谱宽和速度[J]. 热带气象学报, 2018, 34(4): 472-480. [30] 王炳赟, 魏鸣, 范广洲, 等. 1522强台风"彩虹"螺旋雨带中衍生龙卷的超级单体演变与机理研究Ⅱ: 回波结构和钩状回波形成机理[J]. 热带气象学报, 2018, 34(4): 481-488. [31] 周海光. "6.23"江苏阜宁EF4级龙卷超级单体风暴中尺度结构研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 9(61): 3 617-3 639. [32] ZHANG Y, BAI L Q, MENG Z Y, et al. Rapid-scan and polarimetric phased-array radar observations of a tornado in Pearl River Estuary [J]. J Tropical Meteor, 2021, 27. -






 下载:
下载:









 粤公网安备 4401069904700003号
粤公网安备 4401069904700003号