Impact of Madden-Julian Oscillation on Persistent Heavy Rainfall over Hainan Island in October
-
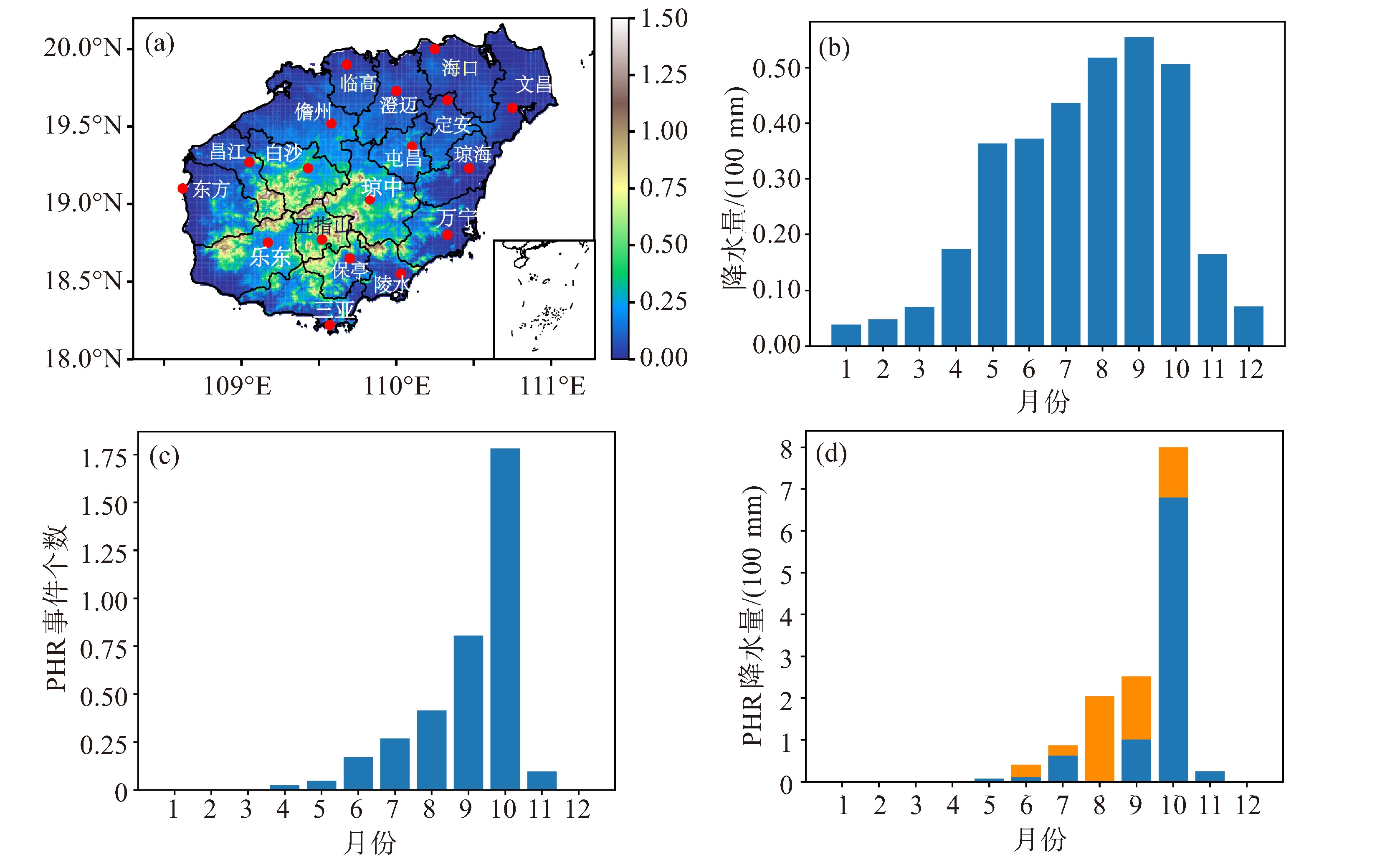
摘要: 本文研究了1979—2019年热带季节内振荡(MJO)对海南岛持续性强降水(PHR)的影响。结果表明,海南岛PHR的降水量和发生频次均以10月最多,且受强MJO的明显调控。当MJO对流位于热带东印度洋-西太平洋(位相3~6)时,海南岛10月持续性强降水偏多;而MJO对流位于热带西印度洋和中太平洋一带(位相7、8、1和2)时,持续性强降水较少。热带东印度洋-西太平洋的MJO对流在海南岛上空引发MJO扰动东风异常,配合其北侧有东北风异常,南侧的南海中北部存在气旋环流异常,与海南岛秋季暴雨的典型环流模态一致,使得低频水汽通量辐合增强,加湿低层大气,有利于海南岛持续性强降水的发生和维持。热带西印度洋和中太平洋一带的MJO对流引发海南岛上空的反气旋环流异常,减弱水汽辐合,不利于低层大气增湿。海洋性大陆附近偏暖的海温以及赤道中东太平洋偏低的海温有助于热带东印度洋-西太平洋MJO对流生成和发展,使得海南岛PHR增强。Abstract: This paper examined the influence of Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) on persistent heavy rainfall (PHR) over Hainan Island from 1979 to 2019. The results reveal that both the precipitation amount and frequency of PHR events peaked in October, exhibiting significant modulation by strong MJO activities. When MJO convection was active over the tropical Eastern Indian Ocean-Western Pacific (phases 3-6), PHR events over Hainan Island increased. Conversely, when MJO convection was located over the tropical Western Indian Ocean and the Central Pacific (phases 7, 8, 1, and 2), PHR events decreased. Active MJO convection in phases 3-6 induced anomalous easterly over Hainan Island, with northeasterly wind anomalies to the north and a cyclonic circulation anomaly over the north-central South China Sea. These conditions were consistent with the typical circulation mode of autumnal rainstorms over Hainan Island, which enhanced the low-frequency moisture flux convergence and thus moistened the lower atmosphere, favoring the occurrence and persistence of PHR over Hainan Island. In contrast, when MJO convection was active in phases 7, 8, 1, and 2, the anticyclonic circulation coupled with MJO convection over Hainan Island could limit moisture flux convergence and inhibit lower atmospheric moistening. The warmer sea surface temperatures (SST) in the tropical Eastern Indian Ocean-Western Pacific and the cooler SST in the tropical Eastern Pacific contributed to the local MJO convection in phases 3-6, which could strengthen the PHR events over Hainan Island.
-
Key words:
- persistent heavy rainfall /
- Madden-Julian Oscillation /
- Hainan Island
-
图 6 (a) 为700~1000 hPa积分的10~90天水汽通量散度异常在MJO不同位相时的合成,单位为(m·s-1)·(g·kg-1)·10-2(其中左边是MJO位相3~6期间,右边是MJO位相7~2期间,黄色是总水汽通量散度,红色是水平平流项,蓝色是辐合-辐散项);(b)和(c)分别为尺度分解后的辐合-辐散项对MJO位相3~6和位相7~2合成结果,单位为(m·s-1)·(g·kg-1)·10-3,其中上标“-”表示低频背景场(>90天),“ ′ ”表示季节内分量(10~90天);“*”表示高频扰动(< 10天),正值为橙色,负值为蓝色。结果为各项在海南岛上(108~111 °E,18~21 °N)的区域平均
-
[1] DING Y H. Summer monsoon rainfalls in China[J]. J Meteor Soc Japan, 1992, 70(1): 373-396. [2] RASUL G, CHAUDHRY Q Z, ZHAO S, et al. A diagnostic study of heavy rainfall in Karachi due to merging of a mesoscale low and a diffused tropical depression during South Asian summer monsoon[J]. Adv Atmos Sci, 2005, 22(3): 375-391. [3] ZHAO S, SUN J. Study on cut-off low-pressure systems with floods over Northeast Asia[J]. Meteor Atmos Phys, 2007, 96(1): 159-180. [4] CHEANG B K. Synoptic features and structures of some equatorial vortices over the South China Sea in the Malaysian region during the winter monsoon, December 1973[J]. Pure Appl Geophys, 1977, 115(5): 1 303-1 333. [5] WANGWONGCHAI A, ZHAO S, ZENG Q. A case study on a strong tropical disturbance and record heavy rainfall in Hat Yai, Thailand during the winter monsoon[J]. Adv Atmos Sci, 2005, 22(4): 436-450. [6] NGUYEN T, UVO C, ROSBJERG D. Relationship between the tropical Pacific and Indian Ocean sea-surface temperature and monthly precipitation over the central highlands, Vietnam[J]. Int J Climatol, 2007, 27(11): 1 439-1 454. [7] 冯文, 周玲丽, 肖潺, 等. 海南岛秋汛期降水的时空分布特点及其环流特征分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2016, 32(4): 533-545. [8] 李勇, 陆日宇, 何金海. 海南岛秋季降水异常对应的热带大尺度环流和海温[J]. 大气科学, 2006, 30(5): 1 034-1 042. [9] FENG X, WU R, CHENG J, et al. Factors for interannual variations of September-October rainfall in Hainan, China[J]. J Climate, 2013, 26 (22): 8 962-8 978. [10] 马学款, 符娇兰, 曹殿斌. 海南2008年秋季持续性暴雨过程的物理机制分析[J]. 气象, 2012, 38(7): 795-803. [11] WANG H, SUN J, ZHAO S. et al. The multiscale factors favorable for a persistent heavy rain event over Hainan Island in October 2010[J]. J Meteor Res, 2016, 30(04): 496-512. [12] 汪汇洁, 孙建华, 赵思雄, 等. 2010年秋季一次海南东海岸特大暴雨的中尺度分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2014, 30(3): 518-532. [13] YOKOI S, MATSUMOTO J. Collaborative effects of cold surge and tropical depression-type disturbance on heavy rainfall in central Vietnam[J]. Mon Wea Rev, 2008, 136(9): 3 275-3 287. [14] CHEN T C, YEN M, TSAY J, et al. Forecast advisory for the late fall heavy rainfall / flood event in central Vietnam developed from diagnostic analysis[J]. Wea Forecasting, 2012, 27(5): 1 155-1 177. [15] CHEN T C, YEN M, TSAY J, et al. Synoptic development of the Hanoi heavy rainfall event during 30-31 October 2008: Multiple-scale processes[J]. Mon Wea Rev, 2012, 140(4): 1 219-1 240. [16] MADDEN R A, JULIAN P R. Detection of a 40-50 day oscillation in the zonal wind in the tropical Pacific[J]. J Atmos Sci, 1971, 28(5): 702-708. [17] MADDEN R A, JULIAN P R. Description of global-scale circulation cells in the tropics with a 40-50 day period[J]. J Atmos Sci, 1972, 29 (6): 1 109-1 123. [18] DONALD A, MEINKE H, POWER B, et al. Near-global impact of the Madden-Julian Oscillation on rainfall[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 2006, 33 (9): L09704. [19] ZHANG C. The Madden-Julian Oscillation[J]. Rev Geophys, 2005, 43(2): RG2003. [20] 李崇银, 潘静, 宋洁. MJO研究新进展[J]. 大气科学, 2013, 37(2): 229-252. [21] 杨广基. 中国东部降水和风场的低频振荡特征[J]. 大气科学, 1992, 16(1): 103-110. [22] 杨辉, 李崇银. 江淮流域夏季严重旱涝与大气季节内振荡[J]. 大气科学进展, 2003, 20(4): 540-553. [23] SEO K H, WANG W, GOTTSCHALCK J, et al. Evaluation of MJO forecast skill from several statistical and dynamical forecast models[J]. J Climate, 2009, 22(9): 2 372-2 388. [24] HSU P C, LI T, YOU L, et al. A spatial-temporal projection method for 10-30-day forecast of heavy rainfall in Southern China[J]. Climate Dyn, 2015, 44(5): 1 227-1 244. [25] 白旭旭, 李崇银, 谭言科, 等. MJO对我国东部春季降水影响的分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2011, 27(6): 814-822. [26] 章丽娜, 林鹏飞, 熊喆, 等. 热带大气季节内振荡对华南前汛期降水的影响[J]. 大气科学, 2011, 35(3): 560-570. [27] 李文铠, 何金海, 祁莉, 等. MJO对华南前汛期降水的影响及其可能机制[J]. 热带气象学报, 2014, 30(5): 983-989. [28] LIN A, LI C, GU D, et al. Impact of tropical intraseasonal oscillations on the precipitation of Guangdong in Junes[J]. J Trop Meteor, 2015, 21(4): 326-336. [29] LIU Y, HSU P C. Long-term changes in wintertime persistent heavy rainfall over southern China contributed by the Madden-Julian Oscillation[J]. Atmos Oceanic Sci Lett, 2019, 12(5): 361-368. [30] 吴慧. 海南省区域性暴雨过程与大气低频振荡的关系[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2017. [31] MA W, ZHU L, FENG X, et al. Impacts of the Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation on the warm-season rainfall over Hainan Island[J]. J Trop Meteor, 2022, 28(4): 457-472. [32] 简茂球, 张春花. 准双周振荡对2010年10月海南持续性暴雨的影响[J]. 热带气象学报, 2013, 29(3): 364-373. [33] QIAO Y, ZHANG C, JIAN M. Role of the 10-20-day oscillation in sustained rainstorms over Hainan, China in October 2010[J]. Adv Atmos Sci, 2015, 32(3): 363-374. [34] WEI X, LIANG P, WU H. Low-frequency circulation and extended-range forecast in connection with autumn extreme heavy rainfall process in Hainan[J]. J Trop Meteor, 2019, 25(04): 543-552. [35] HERSBACH H, BELL B, BERRISFORD P, et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis[J]. Quart J Roy Meteor Soc, 2020, 146(730): 1 999-2 049. [36] WHEELER M, HENDON H. An all-season real-time multivariate MJO index: development of an index for monitoring and prediction[J]. Mon Wea Rev, 2004, 132(8): 1 917-1 932. [37] DUCHON C. Lanczos Filtering in one and two dimensions[J]. J Appl Meteor, 1979, 18(8): 1 016-1 022. [38] HSU P C, LI T. Role of the boundary layer moisture asymmetry in causing the eastward propagation of the Madden-Julian Oscillation[J], J Climate, 2012, 25(14): 4 914-4 931. [39] 冯文, 吴俞, 赵付竹, 等. 海南岛不同强弱秋汛期暴雨的环流形势和动力特征分析[J]. 气象科学, 2017, 37(06): 784-796. [40] 李丽平, 王盘兴, 管兆勇. 热带对流和环流季内振荡强度与海表温度关系对比研究[J]. 大气科学, 2009, 33(4): 771-782. [41] HENDON H, GLICK J. Intraseasonal air-sea interaction in the tropical Indian and Pacific Oceans[J]. J Climate, 1995, 10(4): 647-661. [42] CHEN T C, TSAY J, YEN M, et al. Interannual variation of the late fall rainfall in Central Vietnam[J]. J Climate, 2012, 25(1): 392-413. [43] YEN M, CHEN T C, HU H, et al. Interannual variation of the fall rainfall in Central Vietnam[J]. J Meteor Soc Japan, 2011, 89(A): 259-270. [44] 龙雨青, 张雪莹, 麦博儒. ENSO对MJO传播特征演变的影响[J]. 热带气象学报, 2022, 38(3): 410-421. -






 下载:
下载:









 粤公网安备 4401069904700003号
粤公网安备 4401069904700003号