Analysis of Causes of a Severe Turbulence Event in Xiamen Airspace
-
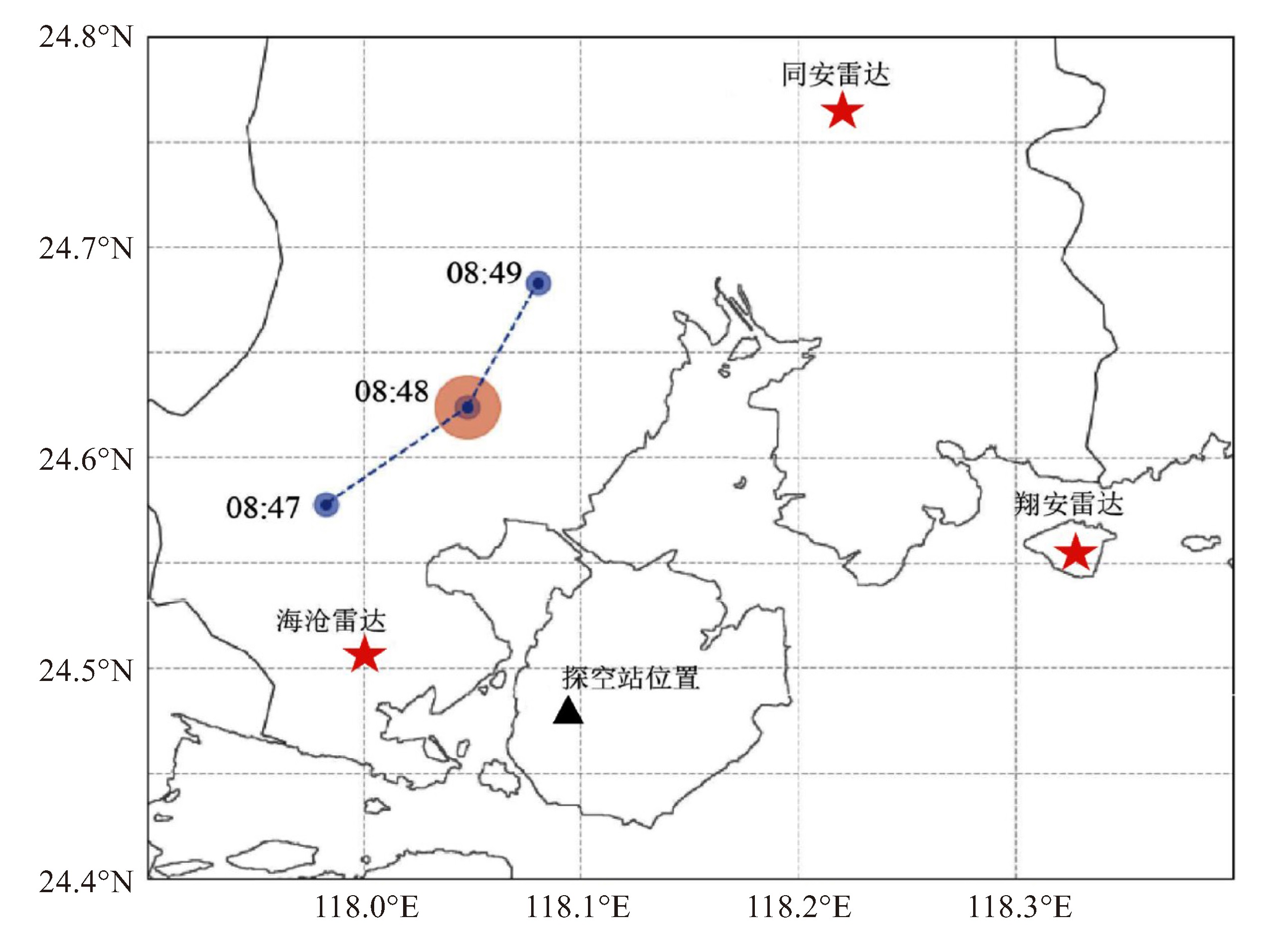
摘要: 利用航空器颠簸报告、福建省厦门空中交通管理站通信导航监视数据、ERA5再分析资料和厦门市气象局布设的X波段双偏振相控阵天气雷达对2023年6月23日08:48(北京时,下同)发生在厦门管制区内2 700 m高度的一起严重颠簸事件进行分析。(1) 本次颠簸事件发生在急流区右侧的西南气流控制中,低层水汽充沛、风场辐合,中层弱冷中心侵入,配合200 hPa辐散,层结不稳定、对流潜在能量高,但垂直风切变小,在地面辐合抬升条件下,有利于出现以脉冲风暴为主的对流天气。颠簸区域位于垂直速度大值区边缘,周边水平和垂直方向上多散度对出现,低层为正涡度气旋式环流,中高层配合反气旋式环流,物理量场的垂直分布为对流天气的发展提供了有利条件。(2) 该航班穿越正在强烈发展的脉冲风暴是此次严重颠簸事件的直接原因。对流单体组合反射率较低,但云中风场有强烈的切变和旋转、空间尺度小,气流条件复杂。X波段相控阵天气雷达探测反演的垂直速度与航空器飞行数据有很好的对应关系,表明云中气流变化导致航空器遭遇严重颠簸。(3)ZDR大值区与强烈的上升气流有明显的对应关系,其后侧存在下沉扰动气流,KDP受粒子密度影响,雷达特征不明显,局部大值区与下沉气流相对应。(4) X波段相控阵雷达组网切变产品(CS、AS、RS)能够反映出小尺度对流单体气流的变化,较对流回波的发展有一定的预警提前量,若切变较强则对流云团后续将继续发展。Abstract: This study analyzed a severe turbulence event that occurred on June 23, 2023, at an altitude of 2 700 meters within the Xiamen airspace, utilizing aircraft turbulence reports, ADS-B data from the Xiamen Air Traffic Management Station, ERA5 reanalysis data, and observations from X-band dualpolarization phased-array weather radar deployed by the Xiamen Meteorological Bureau. The findings revealed that: (1) The turbulence occurred under the influence of southwest airflow on the right side of the jet stream, characterized by abundant moisture and wind field convergence at the low level, and a weak cold center and 200 hPa divergence at the mid level. The atmospheric stratification was unstable, with high potential convective energy and small vertical wind shear. These conditions, coupled with surface convergence and uplift, were conducive to the development of convective weather, particularly pulse storms. The turbulence was located on the periphery of a region with high vertical velocity and was encircled by multiple divergences in both horizontal and vertical directions. The rotation at the low level was positive vorticity cyclonic, while at the mid and upper levels, it became anticyclonic, creating favorable conditions for the development of convective weather. (2) The direct cause of the severe turbulence was the aircraft's passage through a rapidly developing pulse storm. Despite the convective cell's low reflectivity, the wind field within the cloud exhibited strong shear and rotation with a small spatial scale and complex airflow conditions. The vertical velocity measured and inverted by the X-band phased-array weather radar corresponded well with the aircraft's flight data, indicating that changes in cloud airflow led to severe turbulence. (3) A clear correspondence was observed between the high value areas of ZDR and strong updrafts, with sinking disturbance airflow in the rear. KDP values, affected by particle density, presented less distinct radar signatures, with high-value areas sometimes corresponding to descending airflow. (4) X-band phased-array radar shear products (convergence shear, axial shear, and range shear) effectively captured changes in the airflow of small-scale convective cells, providing a measure of early warning for the development of convective echoes. If the shear was strong, the convective cloud clusters were likely to continue developing.
-
Key words:
- flight turbulence /
- X-band /
- phased-array weather radar products
-
-
[1] 阿利曼, 王君, 冯锦明, 等. 中国东部高空颠簸时空分布特征及其与热带中东太平洋海温的关系[J]. 大气科学, 2016, 40(5): 1 073-1 088. [2] SHARMAN R. BROWN B G, DETTLING S. Preliminary results of the NCAR integrated turbulence forecasting algorithm (ITFA) to forecast cat[C]//Preprints, Ninth Conference on Aviation, Range, and Aerospace Meteorology, American Meteorological Society, 2000: 460- 465. [3] 胡壮, 阿利曼, 朱思礼, 等. 中国航空器颠簸报告分析[J]. 中国民航飞行学院学报, 2019, 30(3): 23-25. [4] 金晨曦, 郭文利, 甘璐, 等. 北京地区3000m以下低空颠簸的统计特征及其气象条件分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2019, 35(5): 18-26. [5] 张启凡, 王永忠, 裴柯欣, 等. 基于AMDAR资料的锋区飞机颠簸高发区特征研究[J]. 云南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 30(3): 290-297. [6] 李子良, 黄仪方, 重力惯性波及其不稳定一急流附近飞机颠簸产生的可能机制[J]. 高原气象, 2008, 27(4): 859-865. [7] JAEGER E B, SPRENGER M. A Northern Hemispheric climatology of indices for clear air turbulence in the tropopause region derived from ERA40 reanalysis data[J]. J Geophys, Res, 2007, 112(D20): D20106. [8] 李子良, 黄仪方. 大气湍流引起飞机颠簸的理论分析和数值试验[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2008, 38(6): 889-894. [9] 王永忠, 朱伟军. 边界层急流型重力波飞机颠簸的一种形成机制[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 2001, 24(3): 429-432. [10] 徐海, 黄仪方, 李跃春, 等. 成都-拉萨航线一次严重颠簸过程分析[J]. 中国民航飞行学院学报, 2007, 18(6): 3-7. [11] 吴炎成, 周林, 刘科峰, 等. 基于AMDAR资料应用于中国周边海域飞机颠簸的统计分析[J]. 气象科学, 2014, 34(1): 17-24. [12] 梅婵娟, 张灿, 许可, 等. 山东半岛秋季一次脉冲风暴下击暴流观测分析[J]. 海洋气象学报, 2020, 40(2): 131-139. [13] 陈春元. 中南地区一次飞机颠簸的物理量场分析[J]. 广东气象, 2021, 43(1): 11-14. [14] 魏耀, 张兴敢. 多普勒天气雷达合成切变算法及改进方法的研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(1): 43-47 [15] 王珊珊. 多普勒天气雷达合成切变模块设计[J]. 科技信息, 2007(18): 82-83. [16] MAHALIK M C, SMITH B R, ELMOR K L, et al. Estimates of gradients in radar moments using a linear least-squares derivative technique [J]. Wea Forecasting, 2019, 34(2): 415-434. [17] 赵亮. 龙卷过程中雷达合成切变产品的分析[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 2017, 32(3): 269-275. [18] 刁广秀, 张磊, 孟宪柜, 等. 两次强降水风暴双偏振参量特征分析[J]. 海洋气象学报, 2020, 40(3): 27-36. [19] 刁秀广, 郭飞燕. 2019年8月16日诸城超级单体风暴双偏振参量结构特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 2021, 79(2): 181-195. [20] 黄秀韶, 李芳, 刁秀广. 一次强降水超级单体风暴双偏振参量特征分析[J]. 气象科技, 2022, 50(6): 830-841. [21] 潘佳文, 高丽, 魏鸣, 等. 基于S波段双偏振雷达观测的雹暴偏振特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 2021, 79(1): 168-180. -






 下载:
下载:












 粤公网安备 4401069904700003号
粤公网安备 4401069904700003号