A Review on Extended-range Precipitation Forecast During the First Rainy Season over South China
-
摘要: 华南前汛期降水量大,且常出现持续3天以上、甚至长达10天以上的持续性强降水事件(Persistent Heavy Rainfall Event,PHRE),给该地区带来严重的洪涝灾害,提升前汛期降水的延伸期(提前10~30天或2~6候)预报水平至关重要。重点论述华南降水延伸期预报可预报性的来源,以及当前数值模式、动力-统计释用和机器学习在延伸期预报领域的应用情况,以期了解华南前汛期降水延伸期预报的主要进展。Abstract: The first rainy season precipitation in South China is often characterized by heavy rainfall events lasting for more than 3 days, and even up to 10 days or more. These events, known as Persistent Heavy Rainfall Events (PHRE), result in severe flooding disasters in the region. Improving extended-range (10-30 days or 2-6 weeks in advance) precipitation forecast skill for the first rainy season is crucial. This paper focuses on the precipitation predictability sources of the first rainy season in South china, as well as the current application of numerical models, dynamical-statistical downscaling, and machine learning in the field of extended-range forecasting. The aim is to synthesize major advancements in extended-range precipitation forecasting for the first rainy season in South China.
-
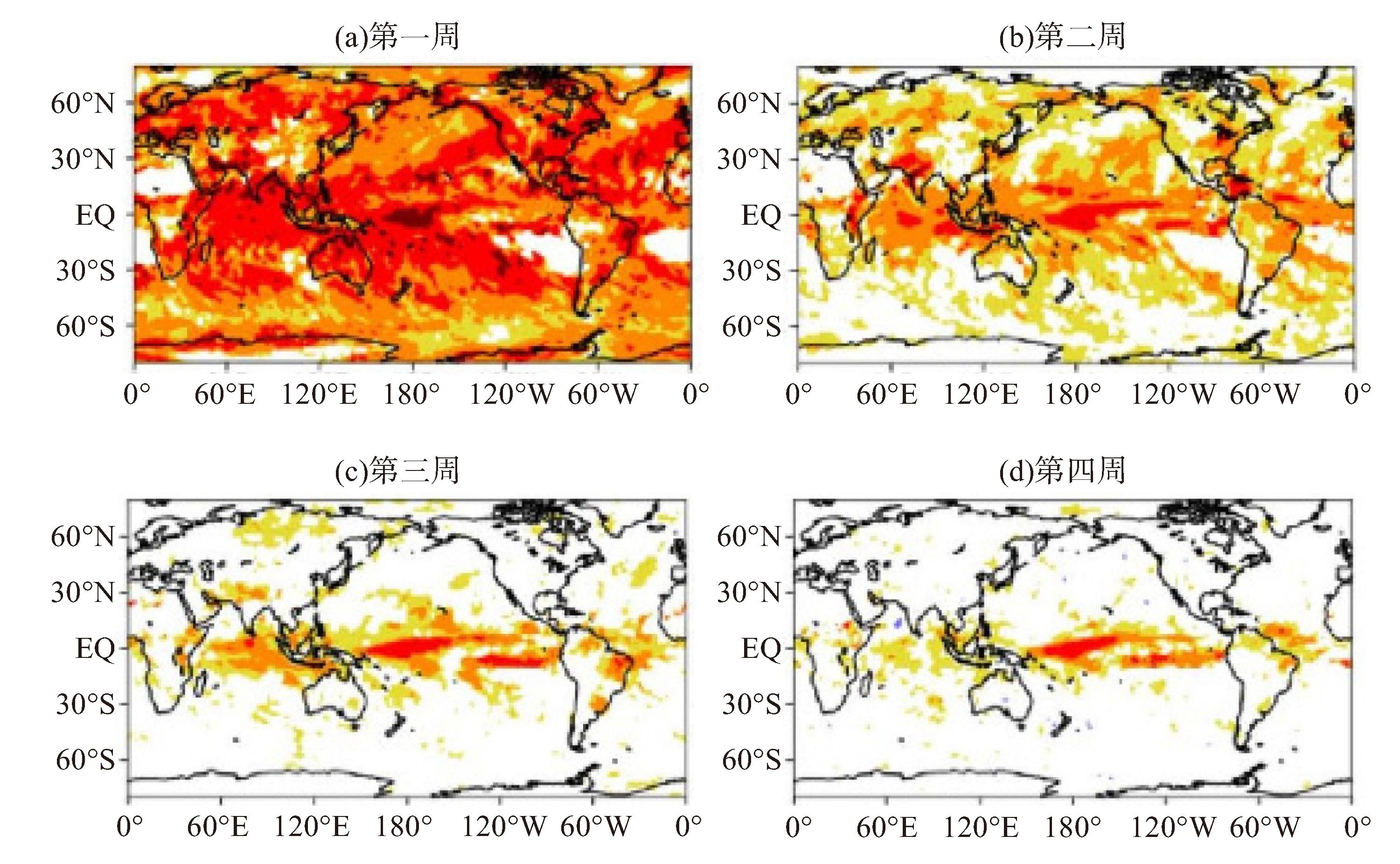
图 1 ECMWF S2S模式集合平均预测全球降水距平的时间相关分布图
预报时效为1~4周[117]。
图 2 ECMWF S2S(第1列)、FuXi-S2S(第2列)、FuXi-S2S和ECMWFS2S的差值(第3列)提前第3~4周 (第1行和第3行)和第5~6周(第2行和第4行)预测总降水量的平均排名概率技能得分(RPSS)(第1行和第2行)和Brier技能得分(BSS)(第3行和第4行)的对比[80]
-
[1] [1] LUO Y, WU M, REN F, et al. Synoptic situations of extreme hourly precipitation over China[J]. J Climate, 2016, 29(24): 8 703-8 719. [2] ZHENG Y, XUE M, LI B, et al. Spatial characteristics of extreme rainfall over China with hourly through 24-hour accumulation periods based on national-level hourly rain gauge data[J]. Adv Atmos Sci, 2016, 33(11): 1 218-1 232. [3] WANG Q W, TAN Z M. Multi‐scale topographic control of southwest vortex formation in Tibetan Plateau region in an idealized simulation [J]. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2014, 119(20): 11 543-11 561. [4] WU M, LUO Y. Mesoscale observational analysis of lifting mechanism of a warm-sector convective system producing the maximal daily precipitation in China mainland during pre-summer rainy season of 2015[J]. J Meteor Res, 2016, 30(5): 719-736. [5] 吴丽姬, 温之平, 贺海晏, 等. 华南前汛期区域持续性暴雨的分布特征及分型[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 46(6): 108-113. [6] 李丽平, 章开美, 王超, 等. 近40年华南前汛期极端降水时空演变特征[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2010, 15(4): 443-450. [7] 郭其蕴, 沙万英. 华南前汛期降水变率的分析[J]. 应用气象学报, 1998, 9(S1): 10-16. [8] 周秀骥, 薛纪善, 陶祖巧, 等. "98"华南暴雨科学试验研究[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2003: 1-10. [9] 邱迪. 华南前汛期持续性暴雨及其与热带大气季节内振荡的联系[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2023. [10] XIE A, CHUNG Y S, LIU X, et al. The interannual variations of the summer monsoon onset overthe South China Sea[J]. Theor Appl Climatol, 1998, 59(3): 201-213. [11] WANG B, LINHO, ZHANG Y, et al. Definition of South China Sea monsoon onset and commencement of the East Asia summer monsoon [J]. J Climate, 2004, 17(4): 699-710. [12] LUO Y, WANG H, ZHANG R, et al. Comparison of rainfall characteristics and convective properties of monsoon precipitation systems over South China and the Yangtze and Huai River basin[J]. J Climate, 2013, 26(1): 110-132. [13] LI Q Q, WANG J H, YANG S, et al. Sub‐seasonal prediction of rainfall over the South China Sea and its surrounding areas during spring-summer transitional season[J]. Int J Climatol, 2020, 40(10): 4326-4346. [14] DING Y, CHAN J C. The East Asian summer monsoon: an overview[J]. Meteorol Atmos Phys, 2005, 89(1-4): 117-142. [15] 林良勋, 吴乃庚, 黄忠, 等. 广东2008年罕见"龙舟水"特点及成因诊断分析[J]. 气象, 2009, 35(4): 43-50 [16] WU H, LI X, SCHUMANN G J P, et al. From recent heavy precipitation in China to a glocal hydrometeorological solution for flood risk prediction[J]. Adv Atmos Sci, 2021, 38(1): 1-7. [17] BAO M. Relationship between persistent heavy rain events in the Huaihe River valley and the distribution pattern of convective activities in the tropical western Pacific warm pool[J]. Adv Atmos Sci, 2008, 25(2): 329-338. [18] 熊文兵, 李江南, 姚才, 等. "05· 6"华南持续性暴雨的成因分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2007, 23(1): 90-97. [19] 慕建利, 王建捷, 李泽椿. 2005年6月华南特大连续性暴雨的环境条件和中尺度扰动分析[J]. 气象学报, 2008, 66(3): 437-451. [20] 王晓芳, 徐明, 闵爱荣, 等. 2010年5月我国南方持续性暴雨过程分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2010, 29(2): 193-199. [21] 吴乃庚, 林良勋, 曾沁, 等. 南海季风爆发前罕见连续3场暴雨特征及成因[J]. 应用气象学报, 2013, 24(2): 129-139. [22] LI X, LUO Y, GUAN Z. The persistent heavy rainfall over southern China in June 2010: Evolution of synoptic systems and the effects of the Tibetan Plateau heating[J]. J Meteor Res, 2014, 28(4): 540-560. [23] CHENG J, ZHAO Y, ZHI R, et al. Meridional circulation dominates the record-breaking"Dragon Boat Water"rainfall over south China in 2022[J]. Front Earth Sci, 2023, 10: 1032313. [24] 覃卫坚, 何莉阳, 蔡悦幸, 等. 近30年华南地区"龙舟水"暴雨研究进展[J]. 气象研究与应用, 2023, 44(1): 1-6 [25] LIU B, ZHU C, XU K, et al. Record-breaking pre-flood rainfall over South China in 2022: Role of historic warming over the Northeast Pacific and Maritime Continent[J]. Climate Dyn, 2023, 61(7): 3 147-3 163. [26] SHENG B, WANG H, LI H, et al. Thermodynamic and dynamic effects of anomalous dragon boat water over South China in 2022[J]. Wea Climate Extrem, 2023, 40: 100560. [27] XIE J H, HSU P C, HU Y M, et al. Disastrous persistent extreme rainfall events of the 2022 pre-flood season in South China: Causes and subseasonal predictions[J]. J Meteor Res, 2023, 37(4): 469-485. [28] BOMPART P, BONTRON G, CELIE S, et al. An operational hydrometeorological forecasting chain for CNR's hydroelectric production needs[J]. Houille Blanche, 2009(5): 54-60. [29] WHITE C J, CARLSEN H, ROBERTSON A W, et al. Potential applications of subseasonal‐to‐seasonal (S2S) predictions[J]. Meteorol Appl, 2017, 24(3): 315-325. [30] PEGION K, KIRTMAN B P, BECKER E, et al. The Subseasonal Experiment (SubX): A multimodel subseasonal prediction experiment[J]. Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2019, 100(10): 2 043-2 060. [31] DOMEISEN D I V, WHITE C J, AFARGAN-GERSTMAN H, et al. Advances in the subseasonal prediction of extreme events: relevant case studies across the globe[J]. Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2022, 103(6): E1473-E1501. [32] WHITE C J, DOMEISEN D I V, ACHARYA N, et al. Advances in the application and utility of subseasonal-to-seasonal predictions[J]. Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2022, 103(6): E1448-E1472. [33] 池艳珍, 何金海, 吴志伟. 华南前汛期不同降水时段的特征分析[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 2005, 28(2): 163-171. [34] 郑彬, 梁建茵, 林爱兰, 等. 华南前汛期的锋面降水和夏季风降水I. 划分日期的确定[J]. 大气科学, 2006, 30(6): 1 207-1 216. [35] 刘瑞鑫, 孙建华, 陈鲍发. 华南暖区暴雨事件的筛选与分类研究[J]. 大气科学, 2019, 43(1): 122-133. [36] ZHENG B, LIN A, HUANG Y. 10-30-Day Subseasonal Features Associated with Multiple and Isolated Persistent Rainfall Events over South China[J]. J Climate, 2023, 36(9): 3 129-3 143. [37] 徐淑爱. 冬季风异常年份的环流特征及其与华南前汛期降水的关系[J]. 热带气象, 1988, 4(3): 263-271. [38] 蔡学湛. 青藏高原雪盖与东亚季风异常对华南前汛期降水的影响[J]. 应用气象学报, 2001, 12(3): 358-367. [39] 赵欢, 张人禾, 温敏. 2013年5月华南强降水与中国南海夏季风爆发[J]. 气象学报, 2015, 73(3): 442-458. [40] 梁建茵, 吴尚森. 广东省汛期旱涝成因和前期影响因子探讨[J]. 热带气象学报, 2001, 16(2): 97-108. [41] 李文铠. 热带大气季节内振荡对华南前汛期降水的影响及其在延伸期预报中的应用[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2014. [42] 李丽平, 许冠宇, 柳艳菊. 2010年华南前汛期低频水汽输送对低频降水的影响[J]. 热带气象学报, 2014, 30(3): 423-431. [43] 陈思, 高建芸, 黄丽娜, 等. 华南前汛期持续性暴雨年代际变化特征及成因[J]. 应用气象学报, 2017, 28(1): 86-97. [44] 蔡学湛, 王岩, 许金镜. 热带对流活动异常对华南前汛期旱涝影响的诊断分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2002, 18(2): 157-164. [45] 郑培慧. 热带气旋与中低纬度系统的相互作用对华南前汛期降水的影响[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2018. [46] 苗春生, 吴志伟, 何金海, 等. 近50年东北冷涡异常特征及其与前汛期华南降水的关系分析[J]. 大气科学, 2006, 30(6): 1 249-1 256. [47] 陈锐丹, 温之平, 陆日宇, 等. 华南6月降水异常及其与东亚—太平洋遥相关的关系[J]. 大气科学, 2012, 36(5): 974-984. [48] 李慧. 华南地区夏季持续性降水事件发生背景与机理[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2019. [49] 刘毓, 陈文. 北半球冬季欧亚遥相关型的变化特征及其对我国气候的影响[J]. 大气科学, 2012, 36(2): 423-432. [50] 许智棋, 陈海山. 近50a华南盛夏降水的季节内差异及大气环流异常特征分析[J]. 气象科学, 2018, 38(1): 1-10. [51] MAO R, GONG D Y, YANG J, et al. Linkage between the Arctic Oscillation and winter extreme precipitation over central-southern China [J]. Climate Res, 2011, 50(2-3): 187-201. [52] 何芬, 赖绍钧, 高建芸, 等. 南极涛动对福建前汛期降水的预测意义[J]. 气象, 2012, 38(4): 432-437. . [53] 黄翀, 张强, 陈晓宏, 等. 珠江流域降水干湿时空特征及气候因子影响研究[J]. 水文, 2017, 37(5): 12-20. [54] 郑菲, 李建平. 前冬南半球环状模对春季华南降水的影响及其机理[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(11): 3 542-3 557. [55] ZHAO L, SONG Y, ZHANG C, et al. A temporal graph convolutional network for traffic prediction[J]. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst, 2020, 21(9): 3 848-3 858. [56] 陈杨瑞雪. 华南前汛期极端降水多尺度特征的统计分析与个例研究[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院, 2018. [57] 邓立平, 王谦谦. 华南前汛期(4~6月)降水异常特征及其与我国近海海温的关系[J]. 热带气象学报, 2002, 18(1): 45-55. [58] 陈艺敏, 钱永甫. 西太平洋暖池海温对华南前汛期降水影响的数值试验[J]. 热带气象学报, 2005, 21(1): 13-23. [59] 强学民, 杨修群. 华南前汛期降水异常与太平洋海表温度异常的关系[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(8): 2 583-2 593. [60] 章开美, 李丽平, 项连东, 等. 华南前汛期极端降水气候变化特征及其与太平洋海温相关关系研究[J]. 气象与减灾研究, 2015, 38(1): 1-7. [61] 吴恒强, 张爱华, 蒋伯仁, 等. 华南前汛期降水与南极海冰变化的关系[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 1998, 21(2): 266-273. [62] 任宏昌. 海温与青藏高原积雪对中国南方夏季降水协同影响及数值模拟研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2017. [63] CHOW K C, LIU Y, CHAN J C L, et al. Effects of surface heating over Indochina and India landmasses on the summer monsoon over South China[J]. Int J Climatol: J Roy Meteorol Soc, 2006, 26(10): 1 339-1 359. [64] 赵玮, 陆尔, 龚理卿, 等. 一种表征南海季风强度的指标及其与华南降水的关系[J]. 大气科学, 2020, 44(1): 3-14. [65] 彭昱忠, 王谦, 元昌安, 等. 数据挖掘技术在气象预报研究中的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(1): 19-27. [66] 徐明, 赵玉春, 王晓芳, 等. 华南前汛期持续性暴雨统计特征及环流分型研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2016, 35(2): 109-118. [67] BROWN J D, DEMARGNE J, SEO D J, et al. The Ensemble Verification System (EVS): A software tool for verifying ensemble forecasts of hydrometeorological and hydrologic variables at discrete locations[J]. Environ Model Softw, 2010, 25(7): 854-872. [68] MESSNER J W, MAYR G J, ZEILEIS A, et al. Heteroscedastic extended logistic regression for postprocessing of ensemble guidance[J]. Mon Wea Rev, 2014, 142(1): 448-456. [69] 蔡芗宁, 马杰, 刘晓波, 等. 气候变化对延伸期预报的影响[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2024, 18(1): 12-19. [70] VITART F, ROBERTSON A W, ANDERSON D L T. Subseasonal to seasonal prediction project: Bridging the gap between weather and climate[J]. Bull World Meteorol Organ, 2012, 61(2): 23-28. [71] LI S, ROBERTSON A W. Evaluation of submonthly precipitation forecast skill from global ensemble prediction systems[J]. Mon Wea Rev, 2015, 143(7): 2 871-2 889. [72] 林爱兰, 纪忠萍, 谷德军, 等. 大气季节内振荡在华南降水预报中的应用[J]. 热带气象学报, 2016, 32(6): 878-889. [73] VITART F, ARDILOUZE C, BONET A, et al. The subseasonal to seasonal (S2S) prediction project database[J]. Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2017, 98(1): 163-173. [74] VITART F, ROBERTSON A W. The sub-seasonal to seasonal prediction project (S2S) and the prediction of extreme events[J]. npj Climate Atmos Sci, 2018, 1(3): 1-7. doi: 10.1038/s41612-018-0013-0 [75] XIE J H, YU J, CHEN H, et al. Sources of subseasonal prediction skill for heatwaves over the Yangtze River Basin revealed from three S2S models[J]. Adv Atmos Sci, 2020, 37(12): 1 435-1 450. [76] MERRYFIELD W J, BAEHR J, BATTÉ L, et al. Current and emerging developments in subseasonal to decadal prediction[J]. Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2020, 101(6): E869-E896. [77] YAN Y, LIU B, ZHU C, et al. Subseasonal forecast barrier of the North Atlantic oscillation in S2S models during the extreme mei-yu rainfall event in 2020[J]. Climate Dyn, 2022, 58(11): 2 913-2 925. [78] MOUATADID S, ORENSTEIN P, FLASPOHLER G, et al. Adaptive bias correction for improved subseasonal forecasting[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 1-13 [79] 张可越, 李娟, 徐邦琪, 等. 中国南方降水及其极端事件的动力-统计相结合延伸期预报[J]. 气象学报, 2023, 81(1): 79-93. [80] CHEN L, ZHONG X, LI H, et al. A machine learning model that outperforms conventional global subseasonal forecast models[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 6425. [81] ZHANG C. Madden-Julian oscillation: Bridging weather and climate[J]. Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2013, 94(12): 1 849-1 870. [82] HSU P C, LEE J Y, HA K J. Influence of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation on rainfall extremes in southern China[J]. Int J Climatol, 2016, 36(3): 1 403-1 412. [83] 章大全, 郑志海, 陈丽娟, 等. 10~30 d延伸期可预报性与预报方法研究进展[J]. 应用气象学报, 2019, 30(4): 416-430. [84] LANG A L, PEGION K, BARNES E A. Introduction to special collection: "Bridging weather and climate: subseasonal‐to‐seasonal (S2S) prediction"[J]. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2020, 125(4): 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD031833 [85] WANG J, WEN Z, WU R, et al. The mechanism of growth of the low-frequency East Asia-Pacific teleconnection and the triggering role of tropical intraseasonal oscillation[J]. Climate Dyn, 2016, 46: 3 965-3 977. [86] LEHTONEN I, KARPECHKO A Y. Observed and modeled tropospheric cold anomalies associated with sudden stratospheric warmings[J]. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2016, 121(4): 1 591-1 610. [87] LIM Y, SON S W, MARSHALL A G, et al. Influence of the QBO on MJO prediction skill in the subseasonal-to-seasonal prediction models [J]. Climate Dyn, 2019, 53(3): 1681-1695. [88] MARIOTTI A, BAGGETT C, BARNES E A, et al. Windows of opportunity for skillful forecasts subseasonal to seasonal and beyond[J]. Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2020, 101(5): E608-E625. [89] JEONG J H, LINDERHOLM H W, WOO S H, et al. Impacts of snow initialization on subseasonal forecasts of surface air temperature for the cold season[J]. J Climate, 2013, 26(6): 1 956-1 972. [90] HU Y M, DING Y H, LIAO F. An improvement on summer regional climate simulation over East China: Importance of data assimilation of soil moisture[J]. Chin Sci Bull, 2010, 55(9): 865-871. [91] 刘婷婷, 陈海山, 蒋薇, 等. 基于土壤湿度和年际增量方法的我国夏季降水预测试验[J]. 大气科学, 2016, 40(3): 591-603. [92] 张人禾, 刘栗, 左志燕. 中国土壤湿度的变异及其对中国气候的影响[J]. 自然杂志, 2016, 38(5): 313-319. [93] SEO E, LEE M I, JEONG J H, et al. Impact of soil moisture initialization on boreal summer subseasonal forecasts: mid-latitude surface air temperature and heat wave events[J]. Climate Dyn, 2019, 52: 1 695-1 709. [94] 周娟, 左志燕, 容新尧. 中国东部土壤湿度异常和厄尔尼诺对中国东部夏季降水的作用比较[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2020, 50(1): 149-160. [95] 叶宇辰, 陈海山, 朱司光, 等. 基于机器学习的中国夏季降水延伸期预报及土壤湿度的可能贡献[J]. 高原气象, 2024, 43(1): 184-198. [96] 胡娅敏, 翟盘茂, 罗晓玲, 等. 2013年华南前汛期持续性强降水的大尺度环流与低频信号特征[J]. 气象学报, 2014, 72(3): 465-477 [97] LI C, LI T, LIN A, et al. Relationship between summer rainfall anomalies and sub-seasonal oscillations in South China[J]. Climate Dyn, 2015, 44(1): 423-439. [98] 李丽萍, 杨春艳, 孔德璇. 华南前汛期典型涝年低频降水特征及其与低频水汽输送的关系[J]. 热带气象学报, 2017, 33(3): 299-312. [99] 苗芮, 温敏, 张人禾. 2010年华南前汛期持续性降水异常与准双周振荡[J]. 热带气象学报, 2017, 33(2): 155-166. [100] WANG X, ZHANG G J. Evaluation of the quasi-biweekly oscillation over the South China Sea in early and late summer in CAM5[J]. J Climate, 2019, 32(1): 69-84. [101] 梁爽. 华南前汛期持续性暴雨10-30d的低频特征及其延伸期预报[D]. 成都: 成都信息工程大学, 2020. [102] 马晨誉. 近30年大气低频振荡对华南前汛期涝旱影响研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2020. [103] 臧钰歆, 徐邦琪, 高迎侠. 10-20d和30-60d低频振荡对华南前汛期持续性暴雨的影响差异及机制研究[J]. 气象学报, 2024, 82(2): 137-154. [104] 孔晓宇, 毛江玉, 吴国雄. 2002年夏季中高纬大气准双周振荡对华南降水的影响[J]. 大气科学, 2017, 41(6): 1 204-1 220. [105] 吴乃庚, 温之平, 邓文剑, 等. 华南前汛期暖区暴雨研究新进展[J]. 气象科学, 2020, 40(5): 605-616. [106] 鲍名. 两次华南持续性暴雨过程中热带西太平洋对流异常作用的比较[J]. 热带气象学报, 2008, 24(1): 27-36. [107] 陈思, 简茂球. 影响华南前汛期降水异常的准双周振荡传播特征[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 54(3): 130-137. [108] 苗芮. 中高纬度和热带系统协同对华南前汛期持续性强降水的影响[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院, 2019. [109] 章丽娜, 林鹏飞, 熊喆, 等. 热带大气季节内振荡对华南前汛期降水的影响[J]. 大气科学, 2011, 35(3): 560-570. [110] 林爱兰, 李春晖, 郑彬, 等. 6月MJO对广东降水调制与直接影响系统的联系[J]. 应用气象学报, 2013, 24(4): 397-406. [111] 李崇银, 周亚萍. 热带大气季节内振荡和ENSO的相互关系[J]. 地球物理学报, 1994, 37(1): 17-26. [112] RIDDLE E E, STONER M B, JOHNSON N C, et al. The impact of the MJO on clusters of wintertime circulation anomalies over the North American region[J]. Climate Dyn, 2013, 40(7): 1 749-1 766. [113] GUSHCHINA D, DEWITTE B. Intraseasonal tropical atmospheric variability associated with the two flavors of El Niño[J]. Mon Wea Rev, 2012, 140(11): 3 669-3 681. [114] PANG B, CHEN Z, WEN Z, et al. Impacts of two types of El Niño on the MJO during boreal winter[J]. Adv Atmos Sci, 2016, 33(8): 979-986. [115] FENG J, LIU P, CHEN W, et al. Contrasting Madden-Julian oscillation activity during various stages of EP and CP El Niños[J]. Atmos Sci Lett, 2015, 16(1): 32-37. [116] CHEN X, LING J, LI C. Evolution of the Madden-Julian oscillation in two types of El Niño[J]. J Climate, 2016, 29(5): 1 919-1 934. [117] LIU J, DA Y, LI T, et al. Impact of ENSO on MJO pattern evolution over the Maritime Continent[J]. J Meteor Res, 2020, 34(6): 1 151-1 166. [118] DE ANDRADE F M, COELHO C A S, CAVALCANTI I F A. Global precipitation hindcast quality assessment of the Subseasonal to Seasonal (S2S) prediction project models[J]. Climate Dyn, 2019, 52(9): 5 451-5 475. [119] LIANG P, LIN H. Sub-seasonal prediction over East Asia during boreal summer using the ECCC monthly forecasting system[J]. Climate Dyn, 2018, 50(3-4): 1 007-1 022. [120] WU J, LI J, ZHU Z, et al. Factors determining the subseasonal prediction skill of summer extreme rainfall over southern China[J]. Climate Dyn, 2023, 60(1): 443-460. [121] LI X, WEI Z, MA L. Prediction abilities of subseasonal‐ to‐ seasonal models for regional rainstorm processes in South China[J]. Int J Climatol, 2023, 43(6): 2 896-2 912. [122] GLAHN H, LOWRY D. The use of Model Output Statistics (MOS) in objective weather forecasting[J]. J Appl Meteorol, 1972, 11(8): 1 203-1 211. [123] 陈丽娟, 李维京, 张培群, 等. 降尺度技术在月降水预报中的应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 2003, 14(6): 648-648. [124] 任宏利, 张培群, 李维京, 等. 提高月预报业务水平的动力相似集合方法[J]. 气象学报, 2014, 72(4): 723-730. [125] 李俊, 杜钧, 陈超君. 降水偏差订正的频率(或面积)匹配方法介绍和分析[J]. 气象, 2014, 40(5): 580-588. [126] 周迪, 陈静, 陈朝平, 等. 暴雨集合预报-观测概率匹配订正法在四川盆地的应用研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2015, 34(2): 97-104. [127] ZHU Y, LUO Y. Precipitation calibration based on the frequency-matching method[J]. Wea Forecasting, 2015, 30(5): 1 109-1 124. [128] 曹萍萍, 肖递祥, 龙柯吉, 等. 基于分位数映射法的四川省ECMWF模式降水预报误差订正分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(4): 666-675. [129] 潘留杰, 薛春芳, 张宏芳, 等. 基于卡尔曼动态频率的ECMWF降水预报订正[J]. 气象, 2022, 48(1): 73-83. [130] 高星星, 潘留杰, 娄盼星, 等. 一种改进的频率匹配法在网格降水预报订正中的应用[J]. 气象, 2023, 49(11): 1 371-1 383. [131] 肖丹, 胡超, 陈宁, 等. 基于频率匹配法的降水预报订正[J]. 气象研究与应用, 2023, 44(3): 28-33. [132] GUDMUNDSSON L, BREMNES J B, HAUGEN J E, et al. Technical note: downscaling RCM precipitation to the station scale using quantile mapping-a comparison of methods[J]. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discusss, 2012, 9(5): 6 185-6 201. [133] CANNON A J, SOBIE S R, MURDOCK T Q. Bias correction of GCM precipitation by quantile mapping: How well do methods pre‐serve changes in quantiles and extremes?[J]. J Climate, 2015, 28(17): 6 938-6 959. [134] 章大全, 陈丽娟. 基于DERF2.0的月平均温度概率订正预报[J]. 大气科学, 2016, 40(5): 1 022-1 032. [135] 雷华锦, 马佳培, 李弘毅, 等. 基于分位数映射法的黑河上游气候模式降水误差订正[J]. 高原气象, 2020, 39(2): 266-279. [136] 梁萍, 丁一汇. 基于季节内振荡的延伸预报试验[J]. 大气科学, 2012, 36(1): 102-116. [137] 吴捷, 任宏利, 许小峰, 等. MJO对我国降水影响的季节调制和动力-统计降尺度预测[J]. 气象, 2018, 44(6): 737-751. [138] SPECQ D, BATTÉ L. Improving subseasonal precipitation forecasts through a statistical-dynamical approach: application to the southwest tropical Pacific[J]. Climate Dyn, 2020, 55(7): 1 913-1 927. [139] 陈锦鹏, 冯业荣, 蒙伟光, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的逐时降水预报订正方法研究[J]. 气象, 2021, 47(1): 60-70. [140] 赵华生, 金龙, 黄小燕, 等. 基于CNN和RF算法的ECMWF降水分级订正预报方法[J]. 气象科技, 2021, 49(3): 419-426. [141] HAMILL T M, WHITAKER J S. Probabilistic quantitative precipitation forecasts based on reforecast analogs: theory and application[J]. Mon Wea Rev, 2006, 134(11): 3 209-3 229. [142] 谢祥洲, 刘军龙, 霍斐斐, 等. 基于机器学习模型的关中地区GPM_IMERG降水数据订正方法[J]. 水电能源科学, 2022, 40(2): 6-9. [143] 谭伟伟, 曾超, 沈焕锋, 等. 基于高斯过程算法的日尺度IMERG降水数据与站点数据的融合研究-以湖北省为例[J]. 华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 54(3): 439-446. [144] BI K, XIE L, ZHANG H, et al. Accurate medium-range global weather forecasting with 3D neural networks[J]. Nature, 2023, 619(7 970): 533-538. [145] CHEN Y, WANG Y, HUANG G, et al. Coupling physical factors for precipitation forecast in China with graph neural network[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 2024, 51(2): 1-12 [146] HAM Y G, KIM J H, LUO J J. Deep learning for multi-year ENSO forecasts[J]. Nature, 2019, 573(7 775): 568-572. [147] LING F, LUO J J, LI Y, et al. Multi-task machine learning improves multi-seasonal prediction of the Indian Ocean Dipole[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(7681): 1-9. [148] TANG Y, DUAN A. Using deep learning to predict the East Asian summer monsoon[J]. Environ Res Lett, 2021, 16(12): 1-10. [149] GUO Q, LUO F, TANG H, et al. Correction of sub-seasonal predictions of summer precipitation in Southwest China based on the Transformer-Seq2Seq-DNN ensemble deep learning model[J]. Theor Appl Climatol, 2023, 152(3): 1 231-1 242. [150] LYU Y, ZHU S, ZHI X, et al. Improving Subseasonal‐To‐Seasonal Prediction of Summer Extreme Precipitation Over Southern China Based on a Deep Learning Method[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 2023, 50(24): e2023GL106245. [151] KIM H, HAM Y G, JOO Y S, et al. Deep learning for bias correction of MJO prediction[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(3 087): 1-7. [152] XIE J H, HSU P C, HU Y, et al. Skillful extended-range forecast of rainfall and extreme events in East China based on deep learning[J]. Wea Forecasting, 2023, 38(3): 467-486. [153] AHN J, LEE J. A new multimodel ensemble method using nonlinear genetic algorithm: An application to boreal winter surface air temperature and precipitation prediction[J]. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2016, 121(16): 9 263-9 277. [154] SONG C, CHEN X, WU P, et al. Combining time varying filtering based empirical mode decomposition and machine learning to predict precipitation from nonlinear series[J]. J Hydrol, 2021, 603: 126914. [155] REICHSTEIN M, CAMPS-VALLS G, STEVENS B, et al. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science [J]. Nature, 2019: 195-204. [156] STAN C, ZHENG C, CHANG E K M, et al. Advances in the prediction of MJO teleconnections in the S2S forecast systems[J]. Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2022, 103(6): E1426-E1447. [157] KRISHNAMURTHY V. Predictability of weather and climate[J]. Earth Space Sci, 2019, 6(7): 1 043-1 056. -






 下载:
下载:


 粤公网安备 4401069904700003号
粤公网安备 4401069904700003号