Research on Simulation of Wide Range PMR based on FY-3G MWRI-RM
-
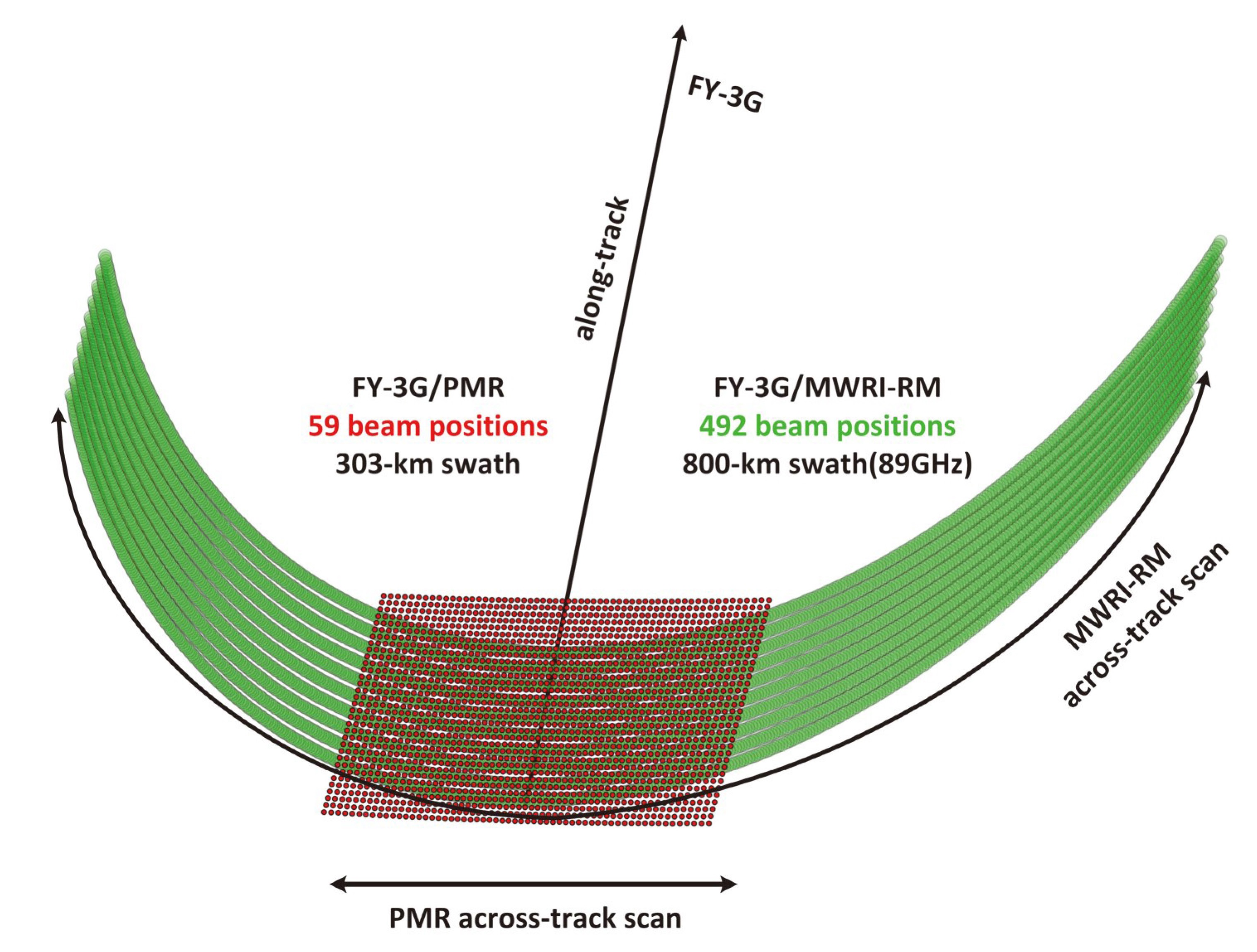
摘要: FY-3降水星搭载的降水测量雷达是我国新一代的主动降水测量载荷,能提供台风、暴雨等灾害性天气系统的监测。降水测量雷达包含Ku和Ka两个波段的观测数据,幅宽较窄但精度高。同平台所搭载的微波成像仪同样具有很好的降水测量的效果,其宽刈幅能够大大提高降水测量的地面覆盖率。本文研究提出了结合DNN模型的方法,通过构建微波成像仪亮温与降水测量雷达反射率因子之间的关系,模拟降水测量雷达的主要测量通道反射信号。同时,通过宽幅观测几何模拟技术,建立与微波成像仪同幅宽的观测几何特性,从而拓宽降水雷达的观测范围,最终获得与微波成像仪同幅宽的降水测量雷达模拟数据。以台风“杜苏芮”和“苏拉”为例的试验测试表明,该方法可将观测幅宽提升1.6倍(300 km提升至800 km),且在降雨区的观测拟合精度均超过85%。试验证明,该方法拟合精度高,能极大拓宽了PMR的视场范围,为降水的观测和反演提供了大量有效的数据。Abstract: The precipitation measurement radar (PMR) carried by FY-3 Mercury is a new generation of active precipitation measurement load in China, which monitors typhoon, rainstorm and other disastrous weather systems. The PMR provides observation data from Ku and Ka bands, with a narrow width but high accuracy. The microwave imager (MERI-RM) installed on the same platform also has good precipitation measurement capabilities, and its wide cutting range can greatly improve the ground coverage for precipitation measurement. This article proposes using the DNN model to establish the relationship between the brightness temperature of the MWRI-RM and the reflectivity factor of the PMR, simulating the reflection signals of the main measurement channels of the PMR. At the same time, by using wide range observation geometry simulation technology, we establish observation geometry characteristics with the same width as the MWRI-RM, thus improving the observation range of the PMR, and ultimately obtain the PMR simulation data with the same width as the MWRI-RM. Through experimental testing of Typhoon Dussuri, it has been shown that this method can increase the observation width by 60% and achieve a fitting accuracy of 85% in rainfall areas.
-
表 1 MWRI-RM各频段详细参数表
序号 中心频率/GHz 极化 带宽/MHz 瞬时视场/(km×km) 主要应用 1 10.65 V,H 180 21×35 洋面强降水,陆表产品 2 18.7 V,H 200 14×23 洋面降水,陆表产品 3 23.8 V,H 400 13×21 洋面水汽总量 4 36.5 V,H 900 9×15 降水,陆表产品 5 50.30 V,H 400 7×11 6 52.61 V,H 400 7×11 7 53.24 V,H 400 7×11 降水、毛毛雨、降雪、融化层高度和厚度 8 53.75 V,H 400 7×11 9 89.0 V,H 400 5×8 洋面和陆地区域降水、降雪,陆表产品 10 118.7503±3.2 V 2×500 4×7 11 118.7503±2.1 V 2×400 4×7 12 118.7503±1.4 V 2×400 4×7 降水、弱降水、降雪、融化层高度和厚度 13 118.7503±1.2 V 2×400 4×7 14 165.5±0.75 V 2×1350 4×6 陆地降水、降雪 15 183.31±2.0 V 2×1500 4×7 16 183.31±3.4 V 2×1500 4×7 降雪,云冰 17 183.31±7 V 2×2000 4×7 表 2 MtPDNN模型多层和单层模拟结果误差统计表
模型模拟结果 相关系数 最大偏差/dBZ 平均偏差/dBZ 均方根误差/dBZ 单层 0.82 4.02 1.32 2.35 多层 0.73 5.54 2.27 3.38 表 3 MtPDNN模型Ka波段模拟结果误差统计表
Ka波段模拟层 相关系数 最大偏差/dBZ 平均偏差/dBZ 均方根误差/dBZ 270层 0.86 2.11 1.13 1.32 280层 0.88 2.72 0.95 1.44 290层 0.90 2.33 1.12 1.76 300层 0.90 2.63 1.25 1.77 310层 0.88 3.18 1.44 2.34 320层 0.86 3.15 1.26 1.72 表 4 MtPDNN模型Ku波段模拟结果误差统计表
Ku波段模拟层 相关系数 最大偏差/dBZ 平均偏差/dBZ 均方根误差/dBZ 270层 0.75 4.81 1.61 2.68 280层 0.81 4.66 1.79 2.79 290层 0.86 4.81 1.74 2.84 300层 0.90 4.85 1.89 2.94 310层 0.89 5.13 1.77 3.01 320层 0.88 4.89 2.18 3.20 -
[1] [1] 刘元波, 傅巧妮, 宋平, 等. 卫星遥感反演降水研究综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 2011, 26(11): 1 162-1 172. [2] 谷松岩, 卢乃锰, 吴琼, 等. FY-3气象卫星降水探测能力分析与展望[J]. 海洋气象学报, 2022, 42(2): 1-10. [3] KOZU T, KAWANISHI T, KUROIWA H, et al. Development of precipitation radar onboard the TRMM satellite[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 102-116. [4] 尹红刚, 吴琼, 谷松岩, 等. 风云三号(03)批降水测量卫星探测能力及应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 2016, 6(3): 55-61. [5] 谷松岩, 张鹏, 陈林, 等. 中国首颗降水测量卫星(风云三号G星)的探测能力概述与展望[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2023, 42(5): 489-498. [6] IUGCHI T, OKI R, SMITH E A, et al. Global precipitation measurement program and the development of dual-frequency precipitation radar [J]. J Commun Res Lab, 2002, 49(2): 37-45. [7] 王咏梅, 任福民, 李维京, 等. 中国台风降水的气候特征[J]. 热带气象学报, 2008, 24(3): 233-238. [8] LIAO L, MENEGHINI R. GPM DPR Retrievals: Algorithm, Evaluation, and Validation[J]. Remote Sens. 2022, 14(4): 843. [9] MASAKI, T, TAKAHASHI N. The Precipitation Rate Retrieval Algorithms for the GPM Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar[J]. J Meteorol Soc Jpn, 2021, 99: 205-237. [10] 姜艳艳. 微波辐射计的SIR图像重建算法[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2010. [11] BACKUS G, GILBERT F. Uniqueness in the inversion of inaccurate gross Earth data[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 1970, Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 266: 123-192. [12] SETHMANN R, BURNS B., HEYGSTEr G C. Spatial resolution improvement of SSM /I data with image restoration techniques[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens, 32(6): 1 144-1 151. [13] 傅云飞, 刘栋, 王雨, 等. 热带测雨卫星综合探测结果之"云娜"台风降水云与非降水云特征[J]. 气象学报, 2007, 65(3): 316-328. [14] 韩丁, 严卫, 叶晶, 等. 基于CloudSat卫星资料分析东太平洋台风的云、降水和热力结构特征[J]. 大气科学, 2013, 37(3): 691-704. [15] 周飞燕, 金林鹏, 董军. 卷积神经网络研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2017, 40(6): 1 229-1 251. [16] 李彦冬, 郝宗波, 雷航. 卷积神经网络研究综述[J]. 计算机应用, 2016, 36(9): 2 508-2 515, 2 565. [17] 朱张莉, 饶元, 吴渊, 等. 注意力机制在深度学习中的研究进展[J]. 中文信息学报, 2019, 33(6): 1-11. [18] 张吉祥, 张祥森, 武长旭, 等. 知识图谱构建技术综述[J]. 计算机工程, 2022, 48(3): 23-37 -






 下载:
下载:









 粤公网安备 4401069904700003号
粤公网安备 4401069904700003号